Norepinephrine is coreleased with serotonin in mouse taste buds
- PMID: 19052199
- PMCID: PMC3331792
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4187-08.2008
Norepinephrine is coreleased with serotonin in mouse taste buds
Abstract
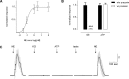
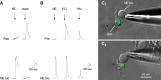
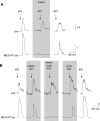
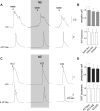
ATP and serotonin (5-HT) are neurotransmitters secreted from taste bud receptor (type II) and presynaptic (type III) cells, respectively. Norepinephrine (NE) has also been proposed to be a neurotransmitter or paracrine hormone in taste buds. Yet, to date, the specific stimulus for NE release in taste buds is not well understood, and the identity of the taste cells that secrete NE is not known. Chinese hamster ovary cells were transfected with alpha(1A) adrenoceptors and loaded with fura-2 ("biosensors") to detect NE secreted from isolated mouse taste buds and taste cells. Biosensors responded to low concentrations of NE (>or=10 nm) with a reliable fura-2 signal. NE biosensors did not respond to stimulation with KCl or taste compounds. However, we recorded robust responses from NE biosensors when they were positioned against mouse circumvallate taste buds and the taste buds were stimulated with KCl (50 mm) or a mixture of taste compounds (cycloheximide, 10 microm; saccharin, 2 mm; denatonium, 1 mm; SC45647, 100 microm). NE biosensor responses evoked by stimulating taste buds were reversibly blocked by prazosin, an alpha(1A) receptor antagonist. Together, these findings indicate that taste bud cells secrete NE when they are stimulated. We isolated individual taste bud cells to identify the origin of NE release. NE was secreted only from presynaptic (type III) taste cells and not receptor (type II) cells. Stimulus-evoked NE release depended on Ca(2+) in the bathing medium. Using dual biosensors (sensitive to 5-HT and NE), we found all presynaptic cells secrete 5-HT and 33% corelease NE with 5-HT.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acid stimulation (sour taste) elicits GABA and serotonin release from mouse taste cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025471. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22028776 Free PMC article.
-
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Reduces Taste-Evoked ATP Secretion from Mouse Taste Buds.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 16;35(37):12714-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0100-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26377461 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate may be an efferent transmitter that elicits inhibition in mouse taste buds.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030662. Epub 2012 Jan 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22292013 Free PMC article.
-
Taste buds as peripheral chemosensory processors.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 Jan;24(1):71-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23261954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transduction and information processing in mammalian taste buds.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Aug;454(5):759-76. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0247-x. Epub 2007 Apr 28. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17468883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in taste receptor cell [Ca2+]i modulate chorda tympani responses to bitter, sweet, and umami taste stimuli.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Dec;108(12):3221-32. doi: 10.1152/jn.00129.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 19. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22993258 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-to-cell communication in intact taste buds through ATP signalling from pannexin 1 gap junction hemichannels.J Physiol. 2009 Dec 15;587(Pt 24):5899-906. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.180083. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19884319 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel processing in mammalian taste buds?Physiol Behav. 2009 Jul 14;97(5):604-8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2009.04.003. Epub 2009 Apr 14. Physiol Behav. 2009. PMID: 19371753 Free PMC article.
-
A taste for ATP: neurotransmission in taste buds.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Dec 18;7:264. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00264. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24385952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in taste receptor cell [Ca2+]i modulate chorda tympani responses to salty and sour taste stimuli.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Dec;108(12):3206-20. doi: 10.1152/jn.00916.2011. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22956787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dvoryanchikov G, Tomchik SM, Chaudhari N. Biogenic amine synthesis and uptake in rodent taste buds. J Comp Neurol. 2007;505:302–313. - PubMed
-
- Finger TE, Danilova V, Barrows J, Bartel DL, Vigers AJ, Stone L, Hellekant G, Kinnamon SC. ATP signaling is crucial for communication from taste buds to gustatory nerves. Science. 2005;310:1495–1499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
