CTLA-4 activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-K) and protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) sustains T-cell anergy without cell death
- PMID: 19052636
- PMCID: PMC2585791
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003842
CTLA-4 activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-K) and protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) sustains T-cell anergy without cell death
Erratum in
- PLoS ONE. 2009;4(1). doi: 10.1371/annotation/5f36e0a6-8e8b-4b33-8e96-a2d53d5c1e46
Abstract
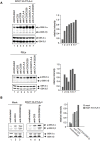
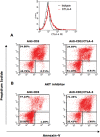
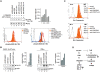
The balance of T-cell proliferation, anergy and apoptosis is central to immune function. In this regard, co-receptor CTLA-4 is needed for the induction of anergy and tolerance. One central question concerns the mechanism by which CTLA-4 can induce T-cell non-responsiveness without a concurrent induction of antigen induced cell death (AICD). In this study, we show that CTLA-4 activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-K) and protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) sustains T-cell anergy without cell death. CTLA-4 ligation induced PI 3K activation as evidenced by the phosphorylation of PKB/AKT that in turn inactivated GSK-3. The level of activation was similar to that observed with CD28. CTLA-4 induced PI 3K and AKT activation also led to phosphorylation of the pro-apoptotic factor BAD as well as the up-regulation of BcL-XL. In keeping with this, CD3/CTLA-4 co-ligation prevented apoptosis under the same conditions where T-cell non-responsiveness was induced. This effect was PI 3K and PKB/AKT dependent since inhibition of these enzymes under conditions of anti-CD3/CTLA-4 co-ligation resulted in cell death. Our findings therefore define a mechanism by which CTLA-4 can induce anergy (and possibly peripheral tolerance) by preventing the induction of cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
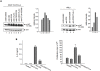
References
-
- Thompson CB, Allison JP. The emerging role of CTLA-4 as an immune attenuator. Immunity. 1997;7:445–450. - PubMed
-
- Rudd CE, Schneider H. Unifying concepts in CD28, ICOS and CTLA-4 co-receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:544–556. - PubMed
-
- Linsley PS, Greene JL, Brady W, Bajorath J, Ledbetter JA, et al. Human B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) bind with similar avidities but distinct kinetics to CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors. Immunity. 1994;1:793–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

