Beyond picomolar affinities: quantitative aspects of noncovalent and covalent binding of drugs to proteins
- PMID: 19053779
- PMCID: PMC2646787
- DOI: 10.1021/jm800498e
Beyond picomolar affinities: quantitative aspects of noncovalent and covalent binding of drugs to proteins
Figures
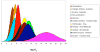

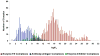
References
-
- Pauling L. The Nature of Forces Between Large Molecules of Biological Interest. Nature. 1948;161:707–709. - PubMed
-
- Congreve M, Murray CW, Blundell TL. Structural Biology and Drug Discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10(13):895–907. - PubMed
-
- Williams SP, Kuyper LF, Pearce KH. Recent Applications of Protein Crystallography and Structure-Guided Drug Design. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9(4):371–380. - PubMed
-
- Gill AL, Frederickson M, Cleasby A, Woodhead SJ, Carr MG, Woodhead AJ, Walker MT, Congreve MS, Devine LA, Tisi D, O’Reilly M, Seavers LC, Davis DJ, Curry J, Anthony R, Padova A, Murray CW, Carr RA, Jhoti H. Identification of Novel p38alpha MAP Kinase Inhibitors Using Fragment-Based Lead Generation. J Med Chem. 2005;48(2):414–426. - PubMed
-
- Kaldor SW, Kalish VJ, Davies JF, 2nd, Shetty BV, Fritz JE, Appelt K, Burgess JA, Campanale KM, Chirgadze NY, Clawson DK, Dressman BA, Hatch SD, Khalil DA, Kosa MB, Lubbehusen PP, Muesing MA, Patick AK, Reich SH, Su KS, Tatlock JH. Viracept (Nelfinavir Mesylate, AG1343): a Potent, Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of HIV-1 Protease. J Med Chem. 1997;40(24):3979–3985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

