Global phenotypic characterization of bacteria
- PMID: 19054113
- PMCID: PMC2704929
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00149.x
Global phenotypic characterization of bacteria
Abstract
The measure of the quality of a systems biology model is how well it can reproduce and predict the behaviors of a biological system such as a microbial cell. In recent years, these models have been built up in layers, and each layer has been growing in sophistication and accuracy in parallel with a global data set to challenge and validate the models in predicting the content or activities of genes (genomics), proteins (proteomics), metabolites (metabolomics), and ultimately cell phenotypes (phenomics). This review focuses on the latter, the phenotypes of microbial cells. The development of Phenotype MicroArrays, which attempt to give a global view of cellular phenotypes, is described. In addition to their use in fleshing out and validating systems biology models, there are many other uses of this global phenotyping technology in basic and applied microbiology research, which are also described.
Figures


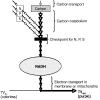
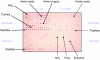
References
-
- Baba T, Huan HC, Datsenko K, Wanner BL, Mori H. The applications of systematic in-frame, single-gene knockout mutant collection of Escherichia coli K-12. Method Mol Biol. 2008;416:183–194. - PubMed
-
- Bibb MJ. Regulation of secondary metabolism in streptomycetes. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:208–215. - PubMed
-
- Bochner B. Methods for detection, identification and speciation of Listerias. US Patent 5,134,063.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

