IFN-gamma expression is up-regulated by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from non-exposed dogs upon Leishmania chagasi promastigote stimulation in vitro
- PMID: 19054575
- PMCID: PMC7126995
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2008.10.324
IFN-gamma expression is up-regulated by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from non-exposed dogs upon Leishmania chagasi promastigote stimulation in vitro
Abstract
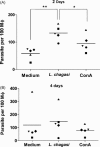
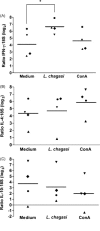
While the response to Leishmania spp. is well characterized in mice and humans, much less is known concerning the canine immune response, particularly soon after exposure to the parasite. Early events are considered to be a determinant of infection outcome. To investigate the dog's early immune response to L. chagasi, an in vitro priming system (PIV) using dog naïve PBMC was established. Until now, dog PIV immune response to L. chagasi has not been assessed. We co-cultivated PBMC primarily stimulated with L. chagasi in vitro with autologous infected macrophages and found that IFN-gamma mRNA is up-regulated in these cells compared to control unstimulated cells. IL-4 and IL-10 mRNA expression by L. chagasi-stimulated PBMC was similar to control unstimulated PBMC when incubated with infected macrophages. Surprisingly, correlation studies showed that a lower IFN-gamma/IL-4 expression ratio correlated with a lower percentage of infection. We propose that the direct correlation between IFN-gamma/IL-4 ratio and parasite load is dependent on the higher correlation of both IFN-gamma and IL-4 expression with lower parasite infection. This PIV system was shown to be useful in evaluating the dog immune response to L. chagasi, and results indicate that a balance between IFN-gamma and IL-4 is associated with control of parasite infection in vitro.
Figures
References
-
- Basu R., Bhaumik S., Basu J.M., Naskar K., De T., Roy S. Kinetoplastid membrane protein-11 DNA vaccination induces complete protection against both pentavalent antimonial-sensitive and -resistant strains of Leishmania donovani that correlates with inducible nitric oxide synthase activity and IL-4 generation: evidence for mixed Th1- and Th2-like responses in visceral leishmaniasis. J. Immunol. 2005;174:7160–7171. - PubMed
-
- Berger S. Lymphocytes as resting cells. In: Jalcoby W.B., Pastan I.H., editors. Vol. 58. Academic Press; 1979. pp. 486–494. (Cell Culture, Methods in Enzymol).
-
- Berrahal F., Mary C., Roze M., Berenger A., Escoffier K., Lamouroux D., Dunan S. Canine leishmaniasis: identification of asymptomatic carriers by polymerase chain reaction and immunoblotting. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996;55:273–277. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C., Stenger S., Rollinghoff M., Solbach W. Cytokine interactions in experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis: interleukin 4 synergizes with interferon-gamma to activate murine macrophages for killing of Leishmania major amastigotes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1991;21:327–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

