Global analysis of protein damage by the lipid electrophile 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal
- PMID: 19054759
- PMCID: PMC2667350
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M800070-MCP200
Global analysis of protein damage by the lipid electrophile 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal
Abstract
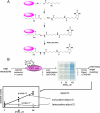
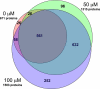
Lipid peroxidation yields a variety of electrophiles, which are thought to contribute to the molecular pathogenesis of diseases involving oxidative stress, yet little is known of the scope of protein damage caused by lipid electrophiles. We identified protein targets of the prototypical lipid electrophile 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) in RKO cells treated with 50 or 100 mum HNE. HNE Michael adducts were biotinylated by reaction with biotinamidohexanoic acid hydrazide, captured with streptavidin, and the captured proteins were resolved by one dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, digested with trypsin, and identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Of the 1500+ proteins identified, 417 displayed a statistically significant increase in adduction with increasing HNE exposure concentration. We further identified 18 biotin hydrazide-modified, HNE-adducted peptides by specific capture using anti-biotin antibody and analysis by high resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. A subset of the identified HNE targets were validated with a streptavidin capture and immunoblotting approach, which enabled detection of adducts at HNE exposures as low as 1 mum. Protein interaction network analysis indicated several subsystems impacted by endogenous electrophiles in oxidative stress, including the 26 S proteasomal and chaperonin containing TCP-1 (CCT) systems involved in protein-folding and degradation, as well as the COP9 signalosome, translation initiation complex, and a large network of ribonucleoproteins. Global analyses of protein lipid electrophile adducts provide a systems-level perspective on the mechanisms of diseases involving oxidative stress.
Figures




References
-
- Ames, B. N. ( 1983) Dietary carcinogens and anticarcinogens. Oxygen radicals and degenerative diseases. Science 221, 1256–1264 - PubMed
-
- Halliwell, B. ( 1994) Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: curiosity, cause, or consequence? Lancet 344, 721–724 - PubMed
-
- Butterfield, D. A. ( 2002) Amyloid beta-peptide (1–42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease brain. A review. Free Radic. Res. 36, 1307–1313 - PubMed
-
- Perry, G., Nunomura, A., Hirai, K., Zhu, X., Perez, M., Avila, J., Castellani, R. J., Atwood, C. S., Aliev, G., Sayre, L. M., Takeda, A., and Smith, M. A. ( 2002) Is oxidative damage the fundamental pathogenic mechanism of Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33, 1475–1479 - PubMed
-
- Beckman, K. B., and Ames, B. N. ( 1998) The free radical theory of aging matures. Physiol. Rev. 78, 547–581 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

