Skeletal muscle growth in young rats is inhibited by chronic exposure to IL-6 but preserved by concurrent voluntary endurance exercise
- PMID: 19057004
- PMCID: PMC2644243
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.90831.2008
Skeletal muscle growth in young rats is inhibited by chronic exposure to IL-6 but preserved by concurrent voluntary endurance exercise
Abstract
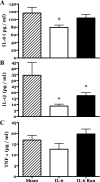
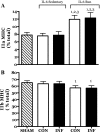
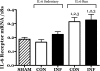
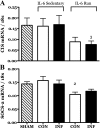
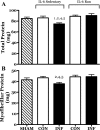
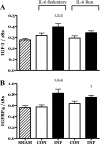
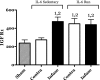
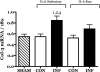
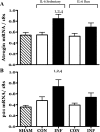
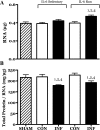
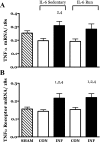
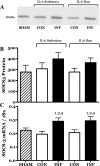
Childhood diseases are often accompanied by chronic inflammation, which is thought to negatively impact growth. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is typically cited as an indicator of inflammation and is linked to impaired growth. This study was designed to isolate and identify potential effects of chronic IL-6 exposure on skeletal muscle growth during development. A second aim was to determine if endurance exercise, thought to antagonize chronic inflammation, would interact with any effects of IL-6. The muscles of one leg of rapidly growing rats were exposed to IL-6 or vehicle for 14 days. Subgroups of IL-6-infused rats were provided access to running wheels. Local IL-6 infusion resulted in approximately 13% muscle growth deficit (myofibrillar protein levels). Exercise (>4,000 m/day) prevented this deficit. IL-6 infusion increased mRNA for suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS3) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and this was not prevented by exercise. IL-6 infusion increased the mRNAs for atrogin, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), and IGF binding protein-4 (IGFBP4), and these effects were mitigated by exercise. Exercise stimulated an increase in total RNA ( approximately 19%) only in the IL-6-infused muscle, suggesting that a compensatory increase in translational capacity was required to maintain muscle growth. This study indicates that IL-6 exposure during periods of rapid growth in young animals can retard growth possibly via interactions with key growth factors. Relatively high volumes of endurance-type exercise do not exacerbate the negative effects of IL-6 and in fact were found to be beneficial in protecting muscle growth.
Figures

References
-
- Adams GR, Haddad F, Baldwin KM. Time course of changes in markers of myogenesis in overloaded rat skeletal muscles. J Appl Physiol 87: 1705–1712, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Adams GR, Haddad F, Bodell PW, Tran PD, Baldwin KM. Combined isometric, concentric and eccentric resistance exercise prevents unloading induced muscle atrophy in rats. J Appl Physiol 103: 1644–1654, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Adams GR, Hather BM, Baldwin KM, Dudley GA. Skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain composition and resistance training. J Appl Physiol 74: 911–915, 1993. - PubMed
-
- Adams GR, McCue SA. Localized infusion of IGF-I results in skeletal muscle hypertrophy in rats. J Appl Physiol 84: 1716–1722, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Al-Khalili L, Bouzakri K, Glund S, Lonnqvist F, Koistinen HA, Krook A. Signaling specificity of interleukin-6 action on glucose and lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle. Mol Endocrinol 20: 3364–3375, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

