Identification, structure, and functional requirement of the Mediator submodule Med7N/31
- PMID: 19057509
- PMCID: PMC2633081
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.254
Identification, structure, and functional requirement of the Mediator submodule Med7N/31
Abstract
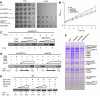
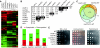
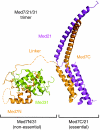
Mediator is a modular multiprotein complex required for regulated transcription by RNA polymerase (Pol) II. Here, we show that the middle module of the Mediator core contains a submodule of unique structure and function that comprises the N-terminal part of subunit Med7 (Med7N) and the highly conserved subunit Med31 (Soh1). The Med7N/31 submodule shows a conserved novel fold, with two proline-rich stretches in Med7N wrapping around the right-handed four-helix bundle of Med31. In vitro, Med7N/31 is required for activated transcription and can act in trans when added exogenously. In vivo, Med7N/31 has a predominantly positive function on the expression of a specific subset of genes, including genes involved in methionine metabolism and iron transport. Comparative phenotyping and transcriptome profiling identify specific and overlapping functions of different Mediator submodules.
Figures


References
-
- Adzhubei AA, Sternberg MJ (1993) Left-handed polyproline II helices commonly occur in globular proteins. J Mol Biol 229: 472–493 - PubMed
-
- Alexa A, Rahnenfuhrer J, Lengauer T (2006) Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure. Bioinformatics 22: 1600–1607 - PubMed
-
- Asturias FJ, Jiang YW, Myers LC, Gustafsson CM, Kornberg RD (1999) Conserved structures of Mediator and RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. Science 283: 985–987 - PubMed
-
- Bäckström S, Elfving N, Nilsson R, Wingsle G, Björklund S (2007) Purification of a plant Mediator from Arabidopsis thaliana identifies PFT1 as the Med25 subunit. Mol Cell 26: 717–729 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

