Neprilysin gene expression requires binding of the amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain to its promoter: implications for Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 19057576
- PMCID: PMC2613207
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2008.222
Neprilysin gene expression requires binding of the amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain to its promoter: implications for Alzheimer disease
Abstract
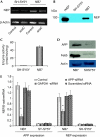
Amyloid beta-peptide (Abeta) accumulation leads to neurodegeneration and Alzheimer disease; however, amyloid metabolism is a dynamic process and enzymic mechanisms exist for Abeta removal. Considerable controversy surrounds whether the intracellular domain of the amyloid precursor protein (AICD) regulates expression of the Abeta-degrading metalloprotease, neprilysin (NEP). By comparing two neuroblastoma cell lines differing substantially in NEP expression, we show by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) that AICD is bound directly to the NEP promoter in high NEP-expresser (NB7) cells but not in low-expresser (SH-SY5Y) cells. The methylation status of the NEP promoter does not regulate expression in these cells, whereas the histone deacetylase inhibitors trichostatin A and valproate partly restore NEP expression and activity in SH-SY5Y cells. ChIP analysis also reveals AICD binding to the NEP promoter in rat primary neurons but not in HUVEC cells. Chromatin remodelling of crucial Alzheimer disease-related genes by valproate could provide a new therapeutic strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


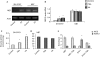
References
-
- Byrne JA, Meara NJ, Rayner AC, Thompson RJ, Knisely AS (2007) Lack of hepatocellular CD10 along bile canaliculi is physiologic in early childhood and persistent in Alagille syndrome. Lab Invest 87: 1138–1148 - PubMed
-
- Cao X, Südhof TC (2001) A transcriptionally active complex of APP with Fe65 and histone acetyltransferase Tip60. Science 293: 115–120 - PubMed
-
- Carson JA, Turner AJ (2002) β-Amyloid catabolism: roles for neprilysin (NEP) and other metallopeptidases? J Neurochem 81: 1–8 - PubMed
-
- Chen AC, Selkoe DJ (2007) Response to: Pardossi-Piquard et al, ‘Presenilin-dependent transcriptional control of the Aβ-degrading enzyme neprilysin by intracellular domains of βAPP and APLP'. Neuron 53: 479–483 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

