Cytoreduction and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from pseudomyxoma peritonei
- PMID: 19058307
- PMCID: PMC2773876
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.6817
Cytoreduction and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from pseudomyxoma peritonei
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the most important aspects of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) that has been accepted as the standard treatment for pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP), with special regard to morbidity, overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS) over 10 years.
Methods: Fifty-three patients affected by PMP underwent cytoreduction (CCR) and HIPEC with a "semi-closed" abdomen technique in our institution. The peritonectomy procedure and completeness of CCR were classified according to Sugarbaker criteria. Preoperative evaluation always included thoracic and abdominal CT scan to stage peritoneal disease and exclude distant metastases. Fifty-one patients in our series were treated with a protocol based on administration of cisplatinum 100 mg/m(2) plus mitomycin C 16 mg/m(2), at a temperature of 41.5 degrees centigrade for 60 min. Anastomoses were always performed at the end of HIPEC. The mean duration of surgery was 12 h including HIPEC. Continuous monitoring of hepatic and renal functions and hydroelectrolytic balance was performed in the postoperative period.
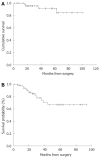
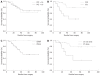
Results: Twenty-four patients presented with postoperative complications: surgical morbidity was observed in 16 patients and 6 patients were re-operated. All complications were successfully treated and no postoperative deaths were observed. Risk factors for postoperative morbidity were considered to be gender, age, body surface, duration of surgery, Peritoneal Cancer Index (PCI) and tumor residual value (CC score). No statistically significant correlation was found during the multivariate analysis: only the CC score was statistically significant. The OS in our experience was 81.8%, with a DFS of 80% at 5 years and of 70% at 10 years.
Conclusion: In our experience, even if HIPEC combined with cytoreductive surgery involves a high risk of morbidity, postoperative complications can be resolved favorably in most cases with correct patient selection and adequate postoperative care, thus minimizing mortality. The association of CCR and HIPEC can be considered as the standard treatment for PMP. The OS and DFS results confirm the validity of this combined approach for the treatment of this rare neoplasm. The impact of preoperative chemotherapy on OS, in our opinion, is due to a major aggressiveness of tumors in treated patients.
Figures
References
-
- Sugarbaker PH. Peritoneal carcinomatosis: natural history and rational therapeutic interventions using intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Res. 1996;81:149–168. - PubMed
-
- Marrelli D, Roviello F, de Manzoni G, Morgagni P, Di Leo A, Saragoni L, De Stefano A, Folli S, Cordiano C, Pinto E. Different patterns of recurrence in gastric cancer depending on Lauren's histological type: longitudinal study. World J Surg. 2002;26:1160–1165. - PubMed
-
- Roviello F, Marrelli D, de Manzoni G, Morgagni P, Di Leo A, Saragoni L, De Stefano A. Prospective study of peritoneal recurrence after curative surgery for gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2003;90:1113–1119. - PubMed
-
- Bando E, Yonemura Y, Takeshita Y, Taniguchi K, Yasui T, Yoshimitsu Y, Fushida S, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Miwa K. Intraoperative lavage for cytological examination in 1,297 patients with gastric carcinoma. Am J Surg. 1999;178:256–262. - PubMed
-
- Pestieau SR, Sugarbaker PH. Treatment of primary colon cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis: comparison of concomitant vs. delayed management. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43:1341–1346; discussion 1347-1348. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

