NADPH oxidases and angiotensin II receptor signaling
- PMID: 19059306
- PMCID: PMC2835147
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.11.003
NADPH oxidases and angiotensin II receptor signaling
Abstract
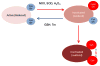
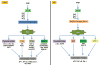
Over the last decade many studies have demonstrated the importance of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by NADPH oxidases in angiotensin II (Ang II) signaling, as well as a role for ROS in the development of different diseases in which Ang II is a central component. In this review, we summarize the mechanism of activation of NADPH oxidases by Ang II and describe the molecular targets of ROS in Ang II signaling in the vasculature, kidney and brain. We also discuss the effects of genetic manipulation of NADPH oxidase function on the physiology and pathophysiology of the renin-angiotensin system.
Figures



References
-
- Agerer F, Lux S, Michel A, Rohde M, Ohlsen K, Hauck CR. Cellular invasion by Staphylococcus aureus reveals a functional link between focal adhesion kinase and cortactin in integrin-mediated internalisation. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:2189–200. - PubMed
-
- Ambasta RK, Schreiber JG, Janiszewski M, Busse R, Brandes RP. Noxa1 is a central component of the smooth muscle NADPH oxidase in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;41:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Ardaillou R, Chansel D, Chatziantoniou C, Dussaule JC. Mesangial AT1 receptors: expression, signaling, and regulation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10 11:S40–6. - PubMed
-
- Banfi B, Clark RA, Steger K, Krause KH. Two novel proteins activate superoxide generation by the NADPH oxidase NOX1. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:3510–3. - PubMed
-
- Barlow RS, White RE. Hydrogen peroxide relaxes porcine coronary arteries by stimulating BKCa channel activity. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:H1283–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

