Quantitative high-throughput analysis of synthetic genetic interactions in Caenorhabditis elegans by RNA interference
- PMID: 19059334
- PMCID: PMC4443778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.11.006
Quantitative high-throughput analysis of synthetic genetic interactions in Caenorhabditis elegans by RNA interference
Abstract
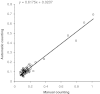
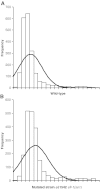
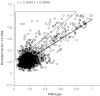
Biological processes are highly dynamic but the current representation of molecular networks is static and largely qualitative. To investigate the dynamic property of genetic networks, a novel quantitative high-throughput method based on RNA interference and capable of calculating the relevance of each interaction, was developed. With this approach, it will be possible to identify not only the components of a network, but also to investigate quantitatively how network and biological processes react to perturbations. As a first application of this method, the genetic interactions of a weak loss-of-function mutation in the gene efl-1/E2F with all the genes of chromosome III were investigated during embryonic development of Caenorhabditis elegans. Fifteen synthetic genetic interactions of efl-1/E2F with the genes of chromosome III were detected, measured and ranked by statistical relevance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A genome-wide RNAi screen for enhancers of par mutants reveals new contributors to early embryonic polarity in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2012 Nov;192(3):929-42. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.143727. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22887819 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics: frontiers of gene function.Nature. 2005 Mar 24;434(7032):444-5. doi: 10.1038/434444a. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15791235 No abstract available.
-
A Synthetic Lethal Screen Identifies a Role for Lin-44/Wnt in C. elegans Embryogenesis.PLoS One. 2015 May 4;10(5):e0121397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121397. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25938228 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput reverse genetics: RNAi screens in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genome Biol. 2001;2(2):REVIEWS1005. doi: 10.1186/gb-2001-2-2-reviews1005. Epub 2001 Jan 31. Genome Biol. 2001. PMID: 11182891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Networks in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011 Dec;21(6):787-98. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.10.003. Epub 2011 Nov 4. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011. PMID: 22054717 Review.
Cited by
-
The contribution of systematic approaches to characterizing the proteins and functions of the endoplasmic reticulum.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Mar 1;5(3):a013284. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013284. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23359093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hartwell L.H., Hopfield J.J., Leibler S., Murray A.W. From molecular to modular cell biology. Nature. 1999;402:C47–C52. - PubMed
-
- NBrowse. http://www.gnetbrowse.org accessed Dicember 2007
-
- Lehner B., Crombie C., Tischler J., Fortunato A., Fraser A.G. Systematic mapping of genetic interactions in Caenorhabditis elegans identifies common modifiers of diverse signaling pathways. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:896–903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

