The farnesoid X receptor regulates transcription of 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in human adrenal cells
- PMID: 19059462
- PMCID: PMC2679217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.11.006
The farnesoid X receptor regulates transcription of 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in human adrenal cells
Abstract
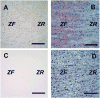
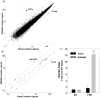
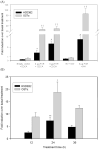
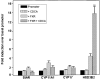
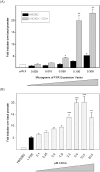
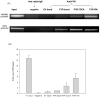
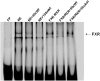
Recent studies have shown that the adrenal cortex expresses high levels of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), but its function remains unknown. Herein, using microarray technology, we tried to identify candidate FXR targeting genes in the adrenal glands, and showed that FXR regulated 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (HSD3B2) expression in human adrenocortical cells. We further demonstrated that FXR stimulated HSD3B2 promoter activity and have defined the cis-element responsible for FXR regulation of HSD3B2 transcription. Transfection of H295R adrenocortical cells with FXR expression vector effectively increased FXR expression levels and additional treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) caused a 25-fold increase in the mRNA for organic solute transporter alpha (OSTalpha), a known FXR target gene. HSD3B2 mRNA levels also increased following CDCA treatment in a concentration-dependent manner. Cells transfected with a HSD3B2 promoter construct and FXR expression vector responded to CDCA with a 20-fold increase in reporter activity compared to control. Analysis of constructs containing sequential deletions of the HSD3B2 promoter suggested a putative regulatory element between -166 and -101. Mutation of an inverted repeat between -137 and -124 completely blocked CDCA/FXR induced reporter activity. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays further confirmed the presence of a FXR response element in the HSD3B2 promoter. In view of the emerging role of FXR agonists as therapeutic treatment of diabetes and certain liver diseases, the effects of such agonists on other FXR expressing tissues should be considered. Our findings suggest that in human adrenal cells, FXR increases transcription and expression of HSD3B2. Alterations in this enzyme would influence the capacity of the adrenal gland to produce corticosteroids.
Figures


References
-
- Bassett MH, Mayhew B, Rehman K, White PC, Mantero F, Arnaldi G, Stewart PM, Bujalska I, Rainey WE. Expression profiles for steroidogenic enzymes in adrenocortical disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:5446–5455. - PubMed
-
- Bassett MH, Suzuki T, Sasano H, De Vries CJ, Jimenez PT, Carr BR, Rainey WE. The orphan nuclear receptor NGFIB regulates transcription of 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. implications for the control of adrenal functional zonation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:37622–37630. - PubMed
-
- Cai SY, Boyer JL. FXR: a target for cholestatic syndromes? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2006b;10:409–421. - PubMed
-
- Chiang JY. Bile acid regulation of gene expression: roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr Rev. 2002;23:443–463. - PubMed
-
- Chiang JY, Kimmel R, Weinberger C, Stroup D. Farnesoid X receptor responds to bile acids and represses cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) transcription. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10918–10924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

