Individual movement behavior, matrix heterogeneity, and the dynamics of spatially structured populations
- PMID: 19060193
- PMCID: PMC2614725
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801725105
Individual movement behavior, matrix heterogeneity, and the dynamics of spatially structured populations
Abstract
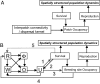
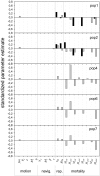
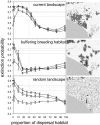
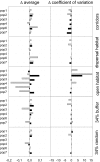
The dynamics of spatially structured populations is characterized by within- and between-patch processes. The available theory describes the latter with simple distance-dependent functions that depend on landscape properties such as interpatch distance or patch size. Despite its potential role, we lack a good mechanistic understanding of how the movement of individuals between patches affects the dynamics of these populations. We used the theoretical framework provided by movement ecology to make a direct representation of the processes determining how individuals connect local populations in a spatially structured population of Iberian lynx. Interpatch processes depended on the heterogeneity of the matrix where patches are embedded and the parameters defining individual movement behavior. They were also very sensitive to the dynamic demographic variables limiting the time moving, the within-patch dynamics of available settlement sites (both spatiotemporally heterogeneous) and the response of individuals to the perceived risk while moving. These context-dependent dynamic factors are an inherent part of the movement process, producing connectivities and dispersal kernels whose variability is affected by other demographic processes. Mechanistic representations of interpatch movements, such as the one provided by the movement-ecology framework, permit the dynamic interaction of birth-death processes and individual movement behavior, thus improving our understanding of stochastic spatially structured populations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hanski I. Metapopulation dynamics. Nature. 1998;396:41–49.
-
- Hanski I, Ovaskainen O. The metapopulation capacity of a fragmented landscape. Nature. 2000;404:755–758. - PubMed
-
- Pulliam HR. Sources, sinks, and population regulation. Am Nat. 1988;132:652–661.
-
- Thomas CD, Kunin WE. The spatial structure of populations. J Anim Ecol. 1999;68:647–657.
-
- Bowler DE, Benton TG. Causes and consequences of animal dispersal strategies: Relating individual behaviour to spatial dynamics. Biol Rev. 2005;80:205–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

