A movement ecology paradigm for unifying organismal movement research
- PMID: 19060196
- PMCID: PMC2614714
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0800375105
A movement ecology paradigm for unifying organismal movement research
Abstract
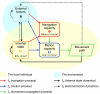
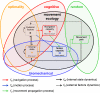
Movement of individual organisms is fundamental to life, quilting our planet in a rich tapestry of phenomena with diverse implications for ecosystems and humans. Movement research is both plentiful and insightful, and recent methodological advances facilitate obtaining a detailed view of individual movement. Yet, we lack a general unifying paradigm, derived from first principles, which can place movement studies within a common context and advance the development of a mature scientific discipline. This introductory article to the Movement Ecology Special Feature proposes a paradigm that integrates conceptual, theoretical, methodological, and empirical frameworks for studying movement of all organisms, from microbes to trees to elephants. We introduce a conceptual framework depicting the interplay among four basic mechanistic components of organismal movement: the internal state (why move?), motion (how to move?), and navigation (when and where to move?) capacities of the individual and the external factors affecting movement. We demonstrate how the proposed framework aids the study of various taxa and movement types; promotes the formulation of hypotheses about movement; and complements existing biomechanical, cognitive, random, and optimality paradigms of movement. The proposed framework integrates eclectic research on movement into a structured paradigm and aims at providing a basis for hypothesis generation and a vehicle facilitating the understanding of the causes, mechanisms, and spatiotemporal patterns of movement and their role in various ecological and evolutionary processes. "Now we must consider in general the common reason for moving with any movement whatever." (Aristotle, De Motu Animalium, 4th century B.C.).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baker RR. The Evolutionary Ecology of Animal Migration. London: Hodder and Stoughton; 1978.
-
- Berg HC. Random Walks in Biology. Princeton, NJ: Princeton Univ Press; 1983.
-
- Swingland IR, Greenwood PJ. The Ecology of Animal Movement. Oxford: Clarendon; 1983.
-
- Stephens DW, Krebs JR. Foraging Theory. Princeton, NJ: Princeton Univ Press; 1986.
-
- Dingle H. Migration: The Biology of Life on the Move. Oxford: Oxford Univ Press; 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

