Variants in MTNR1B influence fasting glucose levels
- PMID: 19060907
- PMCID: PMC2682768
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.290
Variants in MTNR1B influence fasting glucose levels
Abstract
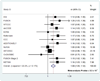
To identify previously unknown genetic loci associated with fasting glucose concentrations, we examined the leading association signals in ten genome-wide association scans involving a total of 36,610 individuals of European descent. Variants in the gene encoding melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) were consistently associated with fasting glucose across all ten studies. The strongest signal was observed at rs10830963, where each G allele (frequency 0.30 in HapMap CEU) was associated with an increase of 0.07 (95% CI = 0.06-0.08) mmol/l in fasting glucose levels (P = 3.2 x 10(-50)) and reduced beta-cell function as measured by homeostasis model assessment (HOMA-B, P = 1.1 x 10(-15)). The same allele was associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes (odds ratio = 1.09 (1.05-1.12), per G allele P = 3.3 x 10(-7)) in a meta-analysis of 13 case-control studies totaling 18,236 cases and 64,453 controls. Our analyses also confirm previous associations of fasting glucose with variants at the G6PC2 (rs560887, P = 1.1 x 10(-57)) and GCK (rs4607517, P = 1.0 x 10(-25)) loci.
Figures

References
-
- Xiang AH, et al. Coordinate changes in plasma glucose and pancreatic beta-cell function in Latino women at high risk for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006;55:1074–1079. - PubMed
-
- Mason CC, Hanson RL, Knowler WC. Progression to type 2 diabetes characterized by moderate then rapid glucose increases. Diabetes. 2007;56:2054–2061. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe RM, et al. Familiality of quantitative metabolic traits in Finnish families with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Finland-United States Investigation of NIDDM Genetics (FUSION) Study investigators. Hum.Hered. 1999;49:159–168. - PubMed
-
- Bouatia-Naji N, et al. A polymorphism within the G6PC2 gene is associated with fasting plasma glucose levels. Science. 2008;320:1085–1088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GR069224/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DK-065978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 077016/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0500539/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 089061/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U54 DA021519/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK065978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MH059160/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G016121/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N02-HL-6-4278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 083948/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DK-080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 079557/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- Z01 HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084729/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DA-021519/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002651/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059160/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DK-062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 077011/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DK069922/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RR-163736/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK029867/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0000649/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- GR072960/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UM1 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL-084729/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HG-02651/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601261/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK069922/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

