Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion
- PMID: 19060908
- PMCID: PMC3725650
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.288
Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion
Abstract
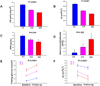
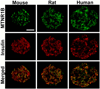
Genome-wide association studies have shown that variation in MTNR1B (melatonin receptor 1B) is associated with insulin and glucose concentrations. Here we show that the risk genotype of this SNP predicts future type 2 diabetes (T2D) in two large prospective studies. Specifically, the risk genotype was associated with impairment of early insulin response to both oral and intravenous glucose and with faster deterioration of insulin secretion over time. We also show that the MTNR1B mRNA is expressed in human islets, and immunocytochemistry confirms that it is primarily localized in beta cells in islets. Nondiabetic individuals carrying the risk allele and individuals with T2D showed increased expression of the receptor in islets. Insulin release from clonal beta cells in response to glucose was inhibited in the presence of melatonin. These data suggest that the circulating hormone melatonin, which is predominantly released from the pineal gland in the brain, is involved in the pathogenesis of T2D. Given the increased expression of MTNR1B in individuals at risk of T2D, the pathogenic effects are likely exerted via a direct inhibitory effect on beta cells. In view of these results, blocking the melatonin ligand-receptor system could be a therapeutic avenue in T2D.
Figures

References
-
- Diabetes Genetics Initiative of Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, L.U., and Novartis Institutes of BioMedical Research, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science. 2007;316:1331–1336. - PubMed
-
- Sladek R, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2007;445:881–885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

