Epinephrine is associated with both erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms
- PMID: 19062003
- PMCID: PMC3742327
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.10.034
Epinephrine is associated with both erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether patients with erectile dysfunction (ED) have a higher incidence of insulin resistance (IR) when compared with controls.
Design: Prospective case-control study.
Setting: Academic medical center.
Patient(s): Twenty-nine nondiabetic men aged 18-66 years were enrolled. Of these, 28 completed the study: 17 had ED, and 11 did not.
Intervention(s): Validated ED questionnaires, examination, serum hormones evaluation, and oral glucose tolerance testing.
Main outcome measure(s): Association of IR with ED.
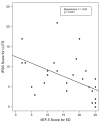
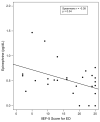
Result(s): The association between worsening degrees of both lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and ED was reaffirmed, as was a potential correlation between the two-epinephrine. There was a negative association between serum levels of epinephrine and scores on the 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Dysfunction for ED (Spearman correlation coefficient = -0.38). On the other hand, men with ED were not more likely to have IR compared with controls.
Conclusion(s): Epinephrine may be the common link between ED and LUTS.
Copyright 2010 American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes severity, metabolic syndrome, and the risk of erectile dysfunction.J Sex Med. 2013 Dec;10(12):3102-9. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12318. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Sex Med. 2013. PMID: 24010555 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction, considering its multiple risk factors.J Sex Med. 2008 Nov;5(11):2662-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.00877.x. Epub 2008 Jun 17. J Sex Med. 2008. PMID: 18564152
-
Lower urinary tract symptoms in patients with erectile dysfunction: analysis of risk factors.J Sex Med. 2006 Jan;3(1):144-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2005.00132.x. J Sex Med. 2006. PMID: 16409228
-
Is the current practice providing an integrated approach to the management of LUTS and ED in primary care? An audit and literature review.J Sex Med. 2007 Nov;4(6):1713-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00598.x. Epub 2007 Oct 1. J Sex Med. 2007. PMID: 17908234 Review.
-
Lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: epidemiology and treatment in the aging man.Curr Urol Rep. 2005 Nov;6(6):445-53. doi: 10.1007/s11934-005-0040-3. Curr Urol Rep. 2005. PMID: 16238919 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing risk of post infection erectile dysfunction following SARS Coronavirus 2 stratified by acute and long COVID, hospitalization status, and vasopressor administration: a U.S. large claims database analysis.Int J Impot Res. 2025 May;37(5):366-371. doi: 10.1038/s41443-024-00913-7. Epub 2024 May 31. Int J Impot Res. 2025. PMID: 38822168
-
Three-Dimensional Proteome-Wide Scale Screening for the 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitor Finasteride: Identification of a Novel Off-Target.J Med Chem. 2021 Apr 22;64(8):4553-4566. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02039. Epub 2021 Apr 12. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33843213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun P, Cameron A, Seftel A, Shabsigh R, Niederberger C, Guay A. Erectile dysfunction—an observable marker of diabetes mellitus? A large national epidemiological study. J Urol. 2006;176:1081–5. - PubMed
-
- Schiel R, Muller UA. Prevalence of sexual disorders in a selection-free diabetic population (JEVIN) Diab Res Clin Pract. 1999;44:115–21. - PubMed
-
- Kashiwagi A, Shinozaki K, Nishio Y, Okamura T, Toda N, Kikkawa R. Free radical production in endothelial cells as a pathological factor for vascular dysfunction in the insulin resistant state. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1999;45:199–203. - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2002;187:356–9. - PubMed
-
- Wheatcroft SB, Williams IL, Shah AM, Kearney MT. Pathophysiological implications of insulin. Diabetes. 2003;20:255–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical