Extracellular sugar modifications provide instructive and cell-specific information for axon-guidance choices
- PMID: 19062279
- PMCID: PMC2765105
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.11.023
Extracellular sugar modifications provide instructive and cell-specific information for axon-guidance choices
Abstract
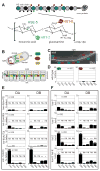
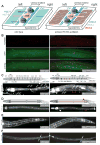
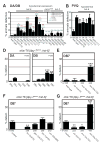
Heparan sulfates (HSs) are extraordinarily complex extracellular sugar molecules that are critical components of multiple signaling systems controlling neuronal development. The molecular complexity of HSs arises through a series of specific modifications, including sulfations of sugar residues and epimerizations of their glucuronic acid moieties. The modifications are introduced nonuniformly along protein-attached HS polysaccharide chains by specific enzymes. Genetic analysis has demonstrated the importance of specific HS-modification patterns for correct neuronal development. However, it remains unclear whether HS modifications provide a merely permissive substrate or whether they provide instructive patterning information during development. We show here with single-cell resolution that highly stereotyped motor axon projections in C. elegans depend on specific HS-modification patterns. By manipulating extracellular HS-modification patterns, we can cell specifically reroute axons, indicating that HS modifications are instructive. This axonal rerouting is dependent on the HS core protein lon-2/glypican and both the axon guidance cue slt-1/Slit and its receptor eva-1. These observations suggest that a changed sugar environment instructs slt-1/Slit-dependent signaling via eva-1 to redirect axons. Our experiments provide genetic in vivo evidence for the "HS code" hypothesis which posits that specific combinations of HS modifications provide specific and instructive information to mediate the specificity of ligand/receptor interactions.
Figures
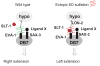
Similar articles
-
A network of HSPG core proteins and HS modifying enzymes regulates netrin-dependent guidance of D-type motor neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 16;8(9):e74908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074908. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24066155 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate modification patterns are required for kal-1-dependent neurite branching in a context-dependent manner in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2013 Mar;3(3):541-52. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.005199. Epub 2013 Mar 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 23451335 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial roles of heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparan sulfates in Caenorhabditis elegans neural development.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 23;9(7):e102919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102919. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25054285 Free PMC article.
-
Migration of neuronal cells along the anterior-posterior body axis of C. elegans: Wnts are in control.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007 Aug;17(4):320-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2007.05.007. Epub 2007 Jul 20. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007. PMID: 17644372 Review.
-
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans: a sugar code for vertebrate development?Development. 2015 Oct 15;142(20):3456-67. doi: 10.1242/dev.098178. Development. 2015. PMID: 26487777 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SDN-1/Syndecan Acts in Parallel to the Transmembrane Molecule MIG-13 to Promote Anterior Neuroblast Migration.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 May 28;5(8):1567-74. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.018770. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26022293 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of glycosaminoglycans as regulators of ligand/receptor complexes.Open Biol. 2018 Oct 3;8(10):180026. doi: 10.1098/rsob.180026. Open Biol. 2018. PMID: 30282658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex cooperative functions of heparan sulfate proteoglycans shape nervous system development in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 Aug 5;4(10):1859-70. doi: 10.1534/g3.114.012591. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 25098771 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi screening of human glycogene orthologs in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and the construction of the C. elegans glycogene database.Glycobiology. 2015 Jan;25(1):8-20. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwu080. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Glycobiology. 2015. PMID: 25091817 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing the role of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in axon guidance in vivo in zebrafish.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1229:469-82. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1714-3_36. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25325973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee JS, Chien CB. When sugars guide axons: insights from heparan sulphate proteoglycan mutants. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:923–935. - PubMed
-
- Van Vactor D, Wall DP, Johnson KG. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and the emergence of neuronal connectivity. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006;16:40–51. - PubMed
-
- Bülow HE, Hobert O. The Molecular Diversity of Glycosaminoglycans Shapes Animal Development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2006 - PubMed
-
- Esko JD, Selleck SB. Order out of chaos: assembly of ligand binding sites in heparan sulfate. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:435–471. - PubMed
-
- Turnbull J, Powell A, Guimond S. Heparan sulfate: decoding a dynamic multifunctional cell regulator. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:75–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

