Multiple phytochrome-interacting bHLH transcription factors repress premature seedling photomorphogenesis in darkness
- PMID: 19062289
- PMCID: PMC2651225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.10.058
Multiple phytochrome-interacting bHLH transcription factors repress premature seedling photomorphogenesis in darkness
Abstract
Background: An important contributing factor to the success of terrestrial flowering plants in colonizing the land was the evolution of a developmental strategy, termed skotomorphogenesis, whereby postgerminative seedlings emerging from buried seed grow vigorously upward in the subterranean darkness toward the soil surface.
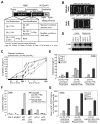
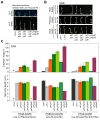
Results: Here we provide genetic evidence that a central component of the mechanism underlying this strategy is the collective repression of premature photomorphogenic development in dark-grown seedlings by several members of the phytochrome (phy)-interacting factor (PIF) subfamily of bHLH transcription factors (PIF1, PIF3, PIF4, and PIF5). Conversely, evidence presented here and elsewhere collectively indicates that a significant component of the mechanism by which light initiates photomorphogenesis upon first exposure of dark-grown seedlings to irradiation involves reversal of this repression by rapid reduction in the abundance of these PIF proteins, through degradation induced by direct interaction of the photoactivated phy molecule with the transcription factors.
Conclusions: We conclude that bHLH transcription factors PIF1, PIF3, PIF4, and PIF5 act as constitutive repressors of photomorphogenesis in the dark, action that is rapidly abrogated upon light exposure by phy-induced proteolytic degradation of these PIFs, allowing the initiation of photomorphogenesis to occur.
Figures


References
-
- Schafer E, Nagy F. Photomorphogenesis in Plants and Bacteria. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer; 2006.
-
- Nagatani A. Light-regulated nuclear localization of phytochromes. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004;7:708–711. - PubMed
-
- Jiao Y, Lau OS, Deng XW. Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:217–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

