Effects of maturation on tympanometric wideband acoustic transfer functions in human infants
- PMID: 19062852
- PMCID: PMC2600624
- DOI: 10.1121/1.2967864
Effects of maturation on tympanometric wideband acoustic transfer functions in human infants
Abstract
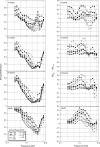
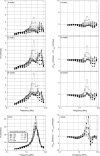
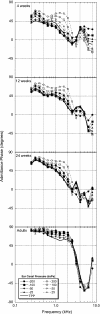
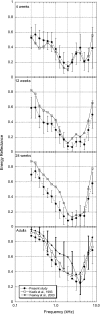
Wideband acoustic transfer function (ATF) measurements of energy reflectance (ER) and admittance magnitude (|Y|) were obtained at varying static ear-canal pressures in 4-, 12-, and 27-week-old infants and young adults. Developmental changes in wideband ATF measurements varied as a function of frequency. For frequencies from 0.25 to 0.75 kHz there was as much as a 30% change in mean ER and mid |Y| with changes in static ear-canal pressure between 4 and 24 weeks of age. From 0.75 to 2 kHz, the effects of pressure produced a small number of significant differences in ER and mid |Y| with age, suggestive of a developmentally stable frequency range. Between 2 and 6 kHz, there were differential effects of pressure for the youngest infants; negative pressures caused increased ER and mid |Y| and positive pressures caused decreased ER and mid |Y|; the magnitude of this effect decreased with age. Findings from this study demonstrate developmental differences in wideband tympanometric ATF measurements in 4-, 12- and 24-week-old infants and provide additional insight on the effects of static ear-canal pressure in the young infant's ear. The maturational effects shown in the experimental data are discussed in light of known age-related anatomical changes in the developing outer and middle ear.
Figures




References
-
- Alaerts, J., Luts, H., and Wouters, J. (2007). “Evaluation of middle ear function in young children: Clinical guidelines for the use of 226- and 1,000-Hz tympanometry,” Otol. Neurotol. 28, 727–732. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, M. (2006). “Choice of probe tone and classification of trace patterns in tympanometry undertaken in early infancy,” Int. J. Audiol. 45, 417–427. - PubMed
-
- Calandruccio, L., Fitzgerald, T. S., and Prieve, B. A. (2006). “Normative multifrequency tympanometry in infants and toddlers,” J. Am. Acad. Audiol 17, 470–480. - PubMed
-
- Eby, T. L., and Nadol, J. B., Jr. (1986). “Postnatal growth of the human temporal bone. Implications for cochlear implants in children,” Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 95, 356–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

