TLR-independent type I interferon induction in response to an extracellular bacterial pathogen via intracellular recognition of its DNA
- PMID: 19064255
- PMCID: PMC3727391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.11.002
TLR-independent type I interferon induction in response to an extracellular bacterial pathogen via intracellular recognition of its DNA
Abstract
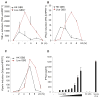
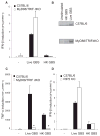
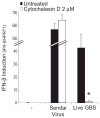
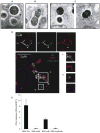
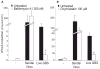
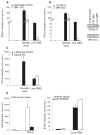
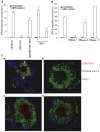
Type I interferon (IFN) is an important host defense cytokine against intracellular pathogens, mainly viruses. In assessing IFN production in response to group B streptococcus (GBS), we find that IFN-beta was produced by macrophages upon stimulation with both heat-killed and live GBS. Exposure of macrophages to heat-killed GBS activated a Toll-like receptor (TLR)-dependent pathway, whereas live GBS activated a TLR/NOD/RIG-like receptor (RLR)-independent pathway. This latter pathway required bacterial phagocytosis, proteolytic bacterial degradation, and phagolysosomal membrane destruction by GBS pore-forming toxins, leading to the release of bacterial DNA into the cytosol. GBS DNA in the cytosol induced IFN-beta production via a pathway dependent on the activation of the serine-threonine kinase TBK1 and phosphorylation of the transcription factor IRF3. Thus, activation of IFN-alpha/-beta production during infection with GBS, commonly considered an extracellular pathogen, appears to result from the interaction of GBS DNA with a putative intracellular DNA sensor or receptor.
Figures
References
-
- Akira S, Sato S. Toll-like receptors and their signaling mechanisms. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003;35:555–562. - PubMed
-
- Baron MJ, Bolduc GR, Goldberg MB, Auperin TC, Madoff LC. Alpha C protein of group B Streptococcus binds host cell surface glycosaminoglycan and enters cells by an actin-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:24714–24723. - PubMed
-
- Berche P, Gaillard JL, Richard S. Invasiveness and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Infection. 1988;16(Suppl 2):S145–S148. - PubMed
-
- Chamaillard M, Hashimoto M, Horie Y, Masumoto J, Qiu S, Saab L, Ogura Y, Kawasaki A, Fukase K, Kusumoto S, et al. An essential role for NOD1 in host recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan containing diaminopimelic acid. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:702–707. - PubMed
-
- Cieslewicz MJ, Kasper DL, Wang Y, Wessels MR. Functional analysis in type Ia group B streptococcus of a cluster of genes involved in extracellular polysaccharide production by diverse species of streptococci. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:139–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

