Strain-specific genetics, anatomy and function of enteric neural serotonergic pathways in inbred mice
- PMID: 19064621
- PMCID: PMC2670081
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.160416
Strain-specific genetics, anatomy and function of enteric neural serotonergic pathways in inbred mice
Abstract
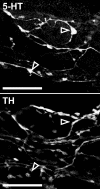
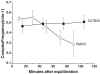
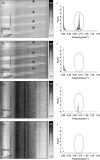
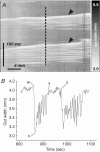
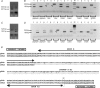
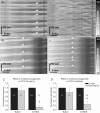
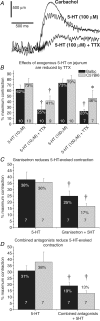
Serotonin (5-HT) powerfully affects small intestinal motility and 5-HT-immunoreactive (IR) neurones are highly conserved between species. 5-HT synthesis in central neurones and gastrointestinal mucosa depends on tissue-specific isoforms of the enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH). RT-PCR identified strain-specific expression of a polymorphism (1473C/G) of the tph2 gene in longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus preparations of C57Bl/6 and Balb/c mice. The former expressed the high-activity C allele, the latter the low-activity G allele. Confocal microscopy was used to examine close contacts between 5-HT-IR varicosities and myenteric neurones immunoreactive for neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS) or calretinin in these two strains. Significantly more close contacts were identified to NOS- (P < 0.05) and calretinin-IR (P < 0.01) neurones in C57Bl/6 jejunum (NOS 1.6 +/- 0.3, n = 52; calretinin 5.2 +/- 0.4, n = 54), than Balb/c jejunum (NOS 0.9 +/- 0.2, n = 78; calretinin 3.5 +/- 0.3, n = 98). Propagating contractile complexes (PCCs) were identified in the isolated jejunum by constructing spatiotemporal maps from video recordings of cannulated segments in vitro. These clusters of contractions usually arose towards the anal end and propagated orally. Regular PCCs were initiated at intraluminal pressures of 6 cmH(2)O, and abolished by tetrodotoxin (1 microm). Jejunal PCCs from C57Bl/6 mice were suppressed by a combination of granisetron (1 microm, 5-HT(3) antagonist) and SB207266 (10 nm, 5-HT(4) antagonist), but PCCs from Balb/c mice were unaffected. There were, however, no strain-specific differences in sensitivity of longitudinal muscle contractions to exogenous 5-HT or blockade of 5-HT(3) and 5-HT(4) receptors. These data associate a genetic difference with significant structural and functional consequences for enteric neural serotonergic pathways in the jejunum.
Figures



Comment in
-
Enteric serotonergic neurones ... finally!J Physiol. 2009 Feb 1;587(3):507. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.167676. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19182271 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Essential roles of enteric neuronal serotonin in gastrointestinal motility and the development/survival of enteric dopaminergic neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 Jun 15;31(24):8998-9009. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6684-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21677183 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Serotonin and Slow-Release 5-Hydroxytryptophan on Gastrointestinal Motility in a Mouse Model of Depression.Gastroenterology. 2019 Aug;157(2):507-521.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.04.022. Epub 2019 May 7. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31071306 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping 5-HT inputs to enteric neurons of the guinea-pig small intestine.Neuroscience. 2007 Mar 16;145(2):556-67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.12.017. Epub 2007 Jan 29. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17261354
-
Review article: serotonin receptors and transporters -- roles in normal and abnormal gastrointestinal motility.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Nov;20 Suppl 7:3-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02180.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15521849 Review.
-
The ever-changing roles of serotonin.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020 Aug;125:105776. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105776. Epub 2020 May 29. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32479926 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Remodeling of Sympathetic Innervation in Atherosclerotic Blood Vessels: Role of Atherosclerotic Disease Progression and Chronic Social Stress.Psychosom Med. 2017 Jan;79(1):59-70. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000360. Psychosom Med. 2017. PMID: 27359178 Free PMC article.
-
Video Imaging and Spatiotemporal Maps to Analyze Gastrointestinal Motility in Mice.J Vis Exp. 2016 Feb 3;(108):53828. doi: 10.3791/53828. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 26862815 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic Mechanisms Regulating the GI Tract: Experimental Evidence and Therapeutic Relevance.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;239:319-342. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_103. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28035530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 Receptor Agonist-induced Actions and Enteric Neurogenesis in the Gut.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014 Jan;20(1):17-30. doi: 10.5056/jnm.2014.20.1.17. Epub 2013 Dec 30. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014. PMID: 24466442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of allergic inflammation by supplementation with 5-hydroxytryptophan.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):L642-60. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00406.2011. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22842218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdu F, Hicks GA, Hennig G, Allen JP, Grundy D. Somatostatin Sst2 receptors inhibit peristalsis in the rat and mouse jejunum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;282:G624–G633. - PubMed
-
- Anlauf M, Schafer MKH, Eiden L, Weihe E. Chemical coding of the human gastrointestinal nervous system: cholinergic, VIPergic, and catecholaminergic phenotypes. J Comp Neurol. 2003;459:90–111. - PubMed
-
- Barbiers M, Timmermans JP, Adriaensen D, Degroodtlasseel MHA, Scheuermann DW. Projections of neurochemically specified neurons in the porcine colon. Histochem Cell Biol. 1995;103:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Blaugrund E, Pham TD, Tennyson VM, Lo L, Sommer L, Anderson DJ, Gershon MD. Distinct subpopulations of enteric neuronal progenitors defined by time of development, sympathoadrenal lineage markers and Mash-1-dependence. Development. 1996;122:309–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

