Brain arteriovenous malformation biology relevant to hemorrhage and implication for therapeutic development
- PMID: 19064791
- PMCID: PMC2677752
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.533216
Brain arteriovenous malformation biology relevant to hemorrhage and implication for therapeutic development
Abstract
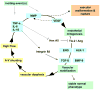
Brain arteriovenous malformations cause intracranial hemorrhage. Molecular characterization of lesional tissue implicates angiogenic (vascular endothelial growth factor, ANG-2, matrix metalloproteinase-9) and inflammatory (cytokines and chemokines) pathways, but the pathogenesis remain obscure and medical therapy is lacking. Macrophage and neutrophil invasion has also been observed in the absence of prior intracranial hemorrhage. Common polymorphisms in interleukin-1beta and activin receptor-like kinase-1 are associated with arteriovenous malformation susceptibility, and polymorphisms in interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and APOE are associated with arteriovenous malformation rupture. These observations suggest that even without a complete understanding of the determinants of arteriovenous malformation development, the recent discoveries of downstream derangements in vascular function and integrity may offer potential targets for therapy development. Furthermore, biomarkers can be established for assessing intracranial hemorrhage risk. Finally, these data will aid in development of model systems for mechanistic testing by development of surrogate phenotypes (microvascular dysplasia) and/or models recapitulating the clinical syndrome of recurrent spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage.
Figures
References
-
- Kim H, Sidney S, McCulloch CE, Poon KY, Singh V, Johnston SC, Ko NU, Achrol AS, Lawton MT, Higashida RT, Young WL. Racial/ethnic differences in longitudinal risk of intracranial hemorrhage in brain arteriovenous malformation patients. Stroke. 2007;38:2430–2437. - PubMed
-
- Young WL, Yang GY. Are there genetic influences on sporadic brain arteriovenous malformations? Stroke. 2004;35:2740–2745. - PubMed
-
- Inoue S, Liu W, Inoue K, Mineharu Y, Takenaka K, Yamakawa H, Abe M, Jafar JJ, Herzig R, Koizumi A. Combination of linkage and association studies for brain arteriovenous malformation. Stroke. 2007;38:1368–1370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

