Human metapneumovirus infections in adults: another piece of the puzzle
- PMID: 19064834
- PMCID: PMC2783624
- DOI: 10.1001/archinte.168.22.2489
Human metapneumovirus infections in adults: another piece of the puzzle
Abstract
Background: Each winter respiratory viruses account for a significant proportion of serious respiratory illness, including hospitalization, in older adults and those with underlying medical conditions. We describe the incidence and clinical impact of human metapneumovirus (HMPV), a newly identified virus, in adults.
Methods: Infection with HMPV was identified in 3 prospectively enrolled adult cohorts (young persons 19-40 years old, healthy adults > or =65 years old, and high-risk adults) and a hospitalized cohort for 4 consecutive winters (November 15 through April 15 for the years 1999 through 2003). The incidence and clinical impact were compared with those of influenza A and respiratory syncytial virus infection in the same groups.
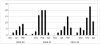
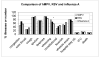
Results: Using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and serologic testing, we identified HMPV infection in 2.2% to 10.5% of the 3 prospectively followed-up outpatient cohorts annually. Asymptomatic infection was common, accounting for at least 38.8% of infections in each of the cohorts. Symptoms, when they occurred, were typical of an upper respiratory tract illness, although a few high-risk persons required hospitalization. Among 1386 hospitalized patients, HMPV was identified in 8.5% (range, 4.4%-13.2%), depending on the year. Dual viral infection was identified in 22.9%. Wheezing was frequent (80%) and more common than with influenza. Twelve percent required intensive care unit admission and 11% ventilatory support, rates similar to those for influenza and respiratory syncytial virus infection.
Conclusions: In adults of all ages, HMPV is a common infection, and, although often asymptomatic, it can result in serious infection that requires hospitalization. Like influenza A and respiratory syncytial virus, HMPV is also a major contributor to the burden of wintertime respiratory illnesses in older adults.
Figures
References
-
- Falsey AR, Hennessey PA, Formica MA, Cox C, Walsh EE. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1749–1759. - PubMed
-
- Dowell SF, Anderson LJ, Gary HE, Jr, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus is an important cause of community-acquired lower respiratory infection among hospitalized adults. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Glezen PW, Greenberg SB, Atmar RL, Piedra PA, Couch RB. Impact of respiratory virus infections on persons with chronic underlying conditions. JAMA. 2000;283:499–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

