Targeted disruption of serine racemase affects glutamatergic neurotransmission and behavior
- PMID: 19065142
- PMCID: PMC2786989
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2008.130
Targeted disruption of serine racemase affects glutamatergic neurotransmission and behavior
Erratum in
- Mol Psychiatry. 2010 Nov;15(11):1122
Abstract
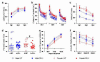
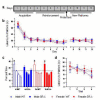
A subset of glutamate receptors that are specifically sensitive to the glutamate analog N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) are molecular coincidence detectors, necessary for activity-dependent processes of neurodevelopment and in sensory and cognitive functions. The activity of these receptors is modulated by the endogenous amino acid D-serine, but the extent to which D-serine is necessary for the normal development and function of the mammalian nervous system was previously unknown. Decreased signaling at NMDA receptors has been implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia based on pharmacological evidence, and several human genes related to D-serine metabolism and glutamatergic neurotransmission have been implicated in the etiology of schizophrenia. Here we show that genetically modified mice lacking the ability to produce D-serine endogenously have profoundly altered glutamatergic neurotransmission, and relatively subtle but significant behavioral abnormalities that reflect hyperactivity and impaired spatial memory, and that are consistent with elevated anxiety.
Figures


References
-
- Johnson JW, Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987;325:529–531. - PubMed
-
- Kleckner NW, Dingledine R. Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus Oocytes. Science. 1988;241:835–837. - PubMed
-
- Fadda E, Danysz W, Wroblewski JT, Costa E. Glycine and D-serine increase the affinity of N-methyl-D-aspartate sensitive glutamate binding sites in rat brain synaptic membranes. Neuropharmacology. 1988;27:1183–1185. - PubMed
-
- Matsui T, Sekiguchi M, Hashimoto A, Tomita U, Nishikawa T, Wada K. Functional comparison of D-serine and glycine in rodents: the effect on cloned NMDA receptors and the extracellular concentration. J Neurochem. 1995;65:454–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

