Ultrasound guidance and monitoring of laser-based fat removal
- PMID: 19065554
- PMCID: PMC2713932
- DOI: 10.1002/lsm.20726
Ultrasound guidance and monitoring of laser-based fat removal
Abstract
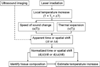
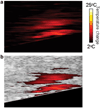
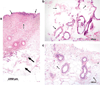
Background and objectives: We report on a study to investigate feasibility of utilizing ultrasound imaging to guide laser removal of subcutaneous fat. Ultrasound imaging can be used to identify the tissue composition and to monitor the temperature increase in response to laser irradiation.
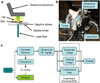
Study design/materials and methods: Laser heating was performed on ex vivo porcine subcutaneous fat through the overlying skin using a continuous wave laser operating at 1,210 nm optical wavelength. Ultrasound images were recorded using a 10 MHz linear array-based ultrasound imaging system.
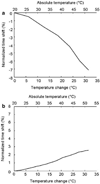
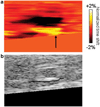
Results: Ultrasound imaging was utilized to differentiate between water-based and lipid-based regions within the porcine tissue and to identify the dermis-fat junction. Temperature maps during the laser exposure in the skin and fatty tissue layers were computed.
Conclusions: Results of our study demonstrate the potential of using ultrasound imaging to guide laser fat removal.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of laser tunnels in laser-assisted lipolysis.Lasers Surg Med. 2009 Dec;41(10):728-37. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20867. Lasers Surg Med. 2009. PMID: 20014256
-
Selective cryolysis: a novel method of non-invasive fat removal.Lasers Surg Med. 2008 Nov;40(9):595-604. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20719. Lasers Surg Med. 2008. PMID: 18951424
-
Comparison of laser-induced damage with forward-firing and diffusing optical fiber during laser-assisted lipoplasty.Lasers Surg Med. 2013 Sep;45(7):437-49. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22155. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Lasers Surg Med. 2013. PMID: 23852719 Free PMC article.
-
Staged ultrasound-guided liposuction for hidden arteriovenous fistulas in obese patients.Vasa. 2018 Aug;47(5):403-407. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000719. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Vasa. 2018. PMID: 30022718 Review.
-
New waves for fat reduction: high-intensity focused ultrasound.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013 Mar;32(1):26-30. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013. PMID: 24049926 Review.
Cited by
-
Study of Interaction of Laser with Tissue Using Monte Carlo Method for 1064nm Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet (Nd:YAG) Laser.J Lasers Med Sci. 2015 Winter;6(1):22-7. J Lasers Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25699164 Free PMC article.
-
Lower eyelid blepharoplasty combined with ultrasound-guided percutaneous diode laser lipolysis: evaluating effectiveness with long-term outcome.Lasers Med Sci. 2023 Feb 27;38(1):78. doi: 10.1007/s10103-023-03739-9. Lasers Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36847890
References
-
- Heymans O, Castus P, Grandjean FX, Van Zele D. Liposuction: Review of the techniques, innovations and applications. Acta Chir Belg. 2006;106(6):647–653. - PubMed
-
- Neira R, Arroyave J, Ramirez H, Ortiz CL, Solarte E, Sequeda F, Gutierrez MI. Fat liquefaction: Effect of low-level laser energy on adipose tissue. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110(3):912–922. discussion 923–915. - PubMed
-
- Alberto G. Submental Nd:Yag laser-assisted liposuction. Lasers Surg Med. 2006;38(3):181–184. - PubMed
-
- Katz B, McBean J. The new laser liposuction for men. Dermatol Ther. 2008;20(6):448–451. - PubMed
-
- Toledo LS, Mauad R. Complications of body sculpture: Prevention and treatment. Clin Plast Surg. 2006;33(1):1–11. v. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

