The renin-angiotensin system and diabetes: an update
- PMID: 19065996
- PMCID: PMC2597759
The renin-angiotensin system and diabetes: an update
Abstract
In the past few years the classical concept of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has experienced substantial conceptual changes. The identification of the renin/prorenin receptor, the angiotensin-converting enzyme homologue ACE2 as an angiotensin peptide processing enzyme, Mas as a receptor for Ang-(1-7) and the possibility of signaling through ACE, have contributed to switch our understanding of the RAS from the classical limited-proteolysis linear cascade to a cascade with multiple mediators, multiple receptors, and multi-functional enzymes. In this review we will focus on the recent findings related to RAS and, in particular, on its role in diabetes by discussing possible interactions between RAS mediators, endothelium function, and insulin signaling transduction pathways as well as the putative role of ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis in disease pathogenesis.
Figures
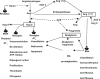


References
-
- Abdalla S, Lother H, Quitterer U. AT1-receptor heterodimers show enhanced G-protein activation and altered receptor sequestration. Nature. 2000;407:94–8. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R. Proinflammatory effects of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: role of additional angiotensin II blockade. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;284:F863–9. - PubMed
-
- Albiston AL, McDowall SG, Matsacos D, et al. Evidence that the angiotensin IV (AT(4)) receptor is the enzyme insulin-regulated ami nopeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:48623–6. - PubMed
-
- Albiston AL, Peck GR, Yeatman HR, et al. Therapeutic targeting of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase: heads and tails? Pharmacol Ther. 2007;116:417–27. - PubMed
-
- Albiston AL, Pederson ES, Burns P, et al. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced learning deficits by LVV-hemorphin-7 in rats in the passive avoidance and water maze paradigms. Behav Brain Res. 2004;154:239–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

