Elevated ATG5 expression in autoimmune demyelination and multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 19066443
- PMCID: PMC2779564
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.5.2.7348
Elevated ATG5 expression in autoimmune demyelination and multiple sclerosis
Abstract
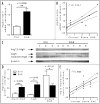
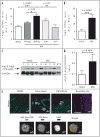
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory central nervous system (CNS) disorder characterized by T cell-mediated demyelination. In MS, prolonged T cell survival and increased T cell proliferation have been linked to disease relapse and progression. Recently, the autophagy-related gene 5 (Atg5) has been shown to modulate T cell survival. In this study, we examined the expression of Atg5 using both a mouse model of autoimmune demyelination as well as blood and brain tissues from MS cases. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of RNA isolated from blood samples of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mice revealed a strong correlation between Atg5 expression and clinical disability.Analysis of protein extracted from these cells confirmed both upregulation and post-translational modification of Atg5, the latter of which was positively correlated with EAE severity. Analysis of RNA extracted from T cells isolated by negative selection indicated that Atg5 expression was significantly elevated in individuals with active relapsing-remitting MS compared to non-diseased controls. Brain tissue sections from relapsing-remitting MS cases examined by immunofluorescent histochemistry suggested that encephalitogenic T cells are a source of Atg5 expression in MS brain samples. Together these data suggest that increased T cell expression of Atg5 may contribute to inflammatory demyelination in MS.
Figures
References
-
- Todaro M, Zeuner A, Stassi G. Role of apoptosis in autoimmunity. J Clin Immunol. 2004;24:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Trapp BD, Nave KA. Multiple sclerosis: an immune or neurodegenerative disorder? Annual review of neuroscience. 2008;31:247–69. - PubMed
-
- Hebb AL, Moore CS, Bhan V, Robertson GS. Targeting apoptosis to treat multiple sclerosis. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2008;5:75–7. - PubMed
-
- Zehntner SP, Bourbonniere L, Moore CS, Morris SJ, Methot D, St Jean M, Lacasse E, Hebb AL, Robertson GS, Durkin J, Gillard JW, Owens T. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis regulates T cell effector function. J Immunol. 2007;179:7553–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
