High-efficiency transduction of the mouse retina by tyrosine-mutant AAV serotype vectors
- PMID: 19066593
- PMCID: PMC2835095
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2008.269
High-efficiency transduction of the mouse retina by tyrosine-mutant AAV serotype vectors
Abstract
Vectors derived from adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) have become important gene delivery tools for the treatment of many inherited ocular diseases in well-characterized animal models. Previous studies have determined that the viral capsid plays an essential role in the cellular tropism and efficiency of transgene expression. Recently, it was shown that phosphorylation of surface-exposed tyrosine residues from AAV2 capsid targets the viral particles for ubiquitination and proteasome- mediated degradation, and mutations of these tyrosine residues lead to highly efficient vector transduction in vitro and in vivo. Because the tyrosine residues are highly conserved in other AAV serotypes, in this study we evaluated the intraocular transduction characteristics of vectors containing point mutations in surface- exposed capsid tyrosine residues in AAV serotypes 2, 8, and 9. Several of these novel AAV mutants were found to display a strong and widespread transgene expression in many retinal cells after subretinal or intravitreal delivery compared with their wild-type counterparts. For the first time, we show efficient transduction of the ganglion cell layer by AAV serotype 8 or 9 mutant vectors, thus providing additional tools besides AAV2 for targeting these cells. These enhanced AAV vectors have a great potential for future therapeutic applications for retinal degenerations and ocular neovascular diseases.
Figures
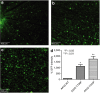

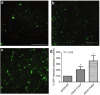
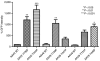


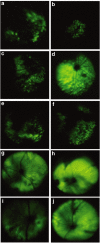
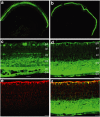
References
-
- Wu Z, Asokan A., and , Samulski RJ. Adeno-associated virus serotypes: vector toolkit for human gene therapy. Mol Ther. 2006;14:316–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- EY08571/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY11087/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY000667/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS036302/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EY018335/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- NS36302/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018335/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY11123/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY0667/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY013729/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008571/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011123/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY07132/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY13729/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 EY000667/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011087/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EY007132/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

