Association of low-energy femoral fractures with prolonged bisphosphonate use: a case control study
- PMID: 19066707
- PMCID: PMC4415520
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-008-0805-x
Association of low-energy femoral fractures with prolonged bisphosphonate use: a case control study
Abstract
Summary: Recent evidence has linked long-term bisphosphonate use with insufficiency fractures of the femur in postmenopausal women. In this case-control study, we have identified a significant association between a unique fracture of the femoral shaft, a transverse fracture in an area of thickened cortices, and long-term bisphosphonate use. Further studies are warranted.
Introduction: Although clinical trials confirm the anti-fracture efficacy of bisphosphonates over 3-5 years, the long-term effects of bisphosphonate use on bone metabolism are unknown. Femoral insufficiency fractures in patients on prolonged treatment have been reported.
Methods: We performed a retrospective case-control study of postmenopausal women who presented with low-energy femoral fractures from 2000 to 2007. Forty-one subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fracture cases were identified and matched by age, race, and body mass index to one intertrochanteric and femoral neck fracture each.
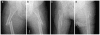
Results: Bisphosphonate use was observed in 15 of the 41 subtrochanteric/shaft cases, compared to nine of the 82 intertrochanteric/femoral neck controls (Mantel-Haenszel odds ratio (OR), 4.44 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.77-11.35]; P = 0.002). A common X-ray pattern was identified in ten of the 15 subtrochanteric/shaft cases on a bisphosphonate. This X-ray pattern was highly associated with bisphosphonate use (OR, 15.33 [95% CI 3.06-76.90]; P < 0.001). Duration of bisphosphonate use was longer in subtrochanteric/shaft cases compared to both hip fracture controls groups (P = 0.001).
Conclusions: We found a significantly greater proportion of patients with subtrochanteric/shaft fractures to be on long-term bisphosphonates than intertrochanteric/femoral neck fractures. Bisphosphonate use was highly associated with a unique X-ray pattern. Further studies are warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Association of low-energy femoral fractures with prolonged bisphosphonate use: a case--control study.Osteoporos Int. 2009 Aug;20(8):1457-8. doi: 10.1007/s00198-009-0955-5. Epub 2009 May 13. Osteoporos Int. 2009. PMID: 19436933 No abstract available.
References
-
- Liberman UA, Weiss SR, Broll J, Minne HW, Quan H, Bell NH, Rodriguez-Portales J, Downs RW, Jr, Dequeker J, Favus M. Effect of oral alendronate on bone mineral density and the incidence of fractures in postmenopausal osteoporosis. The Alendronate Phase III Osteoporosis Treatment Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1437–1443. - PubMed
-
- Bone HG, Hosking D, Devogelaer JP, Tucci JR, Emkey RD, Tonino RP, Rodriguez-Portales JA, Downs RW, Gupta J, Santora AC, Liberman UA. Alendronate Phase III Osteoporosis Treatment Study Group (2004) Ten years’ experience with alendronate for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 350:1189–1199. - PubMed
-
- Black DM, Schwartz AV, Ensrud KE, Cauley JA, Levis S, Quandt SA, Satterfield S, Wallace RB, Bauer DC, Palermo L, Wehren LE, Lombardi A, Santora AC, Cummings SR FLEX Research Group. Effects of continuing or stopping alendronate after 5 years of treatment: the Fracture Intervention Trial Long-term Extension (FLEX): a randomized trial. JAMA. 2006;296:2927–2938. - PubMed
-
- Odvina CV, Zerwekh JE, Rao DS, Maalouf N, Gottschalk FA, Pak CY. Severely suppressed bone turnover: a potential complication of alendronate therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:1294–1301. - PubMed
-
- Goh SK, Yang KY, Koh JS, Wong MK, Chua SY, Chua DT, Howe TS. Subtrochanteric insufficiency fractures in patients on alendronate therapy: a caution. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:349–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

