Quality assurance of PASADENA hyperpolarization for 13C biomolecules
- PMID: 19067009
- PMCID: PMC2664864
- DOI: 10.1007/s10334-008-0154-y
Quality assurance of PASADENA hyperpolarization for 13C biomolecules
Abstract
Object: Define MR quality assurance procedures for maximal PASADENA hyperpolarization of a biological (13)C molecular imaging reagent.
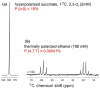
Materials and methods: An automated PASADENA polarizer and a parahydrogen generator were installed. (13)C enriched hydroxyethyl acrylate, 1-(13)C, 2,3,3-d(3) (HEA), was converted to hyperpolarized hydroxyethyl propionate, 1-(13)C, 2,3,3-d(3) (HEP) and fumaric acid, 1-(13)C, 2,3-d(2) (FUM) to hyperpolarized succinic acid, 1-(13)C, 2,3-d(2) (SUC), by reaction with parahydrogen and norbornadiene rhodium catalyst. Incremental optimization of successive steps in PASADENA was implemented. MR spectra and in vivo images of hyperpolarized (13)C imaging agents were acquired at 1.5 and 4.7 T.
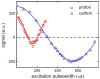
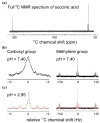
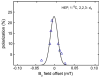
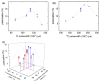
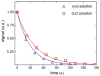
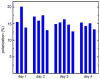
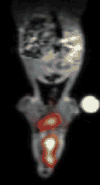
Results: Application of quality assurance (QA) criteria resulted in incremental optimization of the individual steps in PASADENA implementation. Optimal hyperpolarization of HEP of P = 20% was achieved by calibration of the NMR unit of the polarizer (B (0) field strength +/- 0.002 mT). Mean hyperpolarization of SUC, P = [15.3 +/- 1.9]% (N = 16) in D (2)O, and P = [12.8 +/- 3.1]% (N = 12) in H (2)O, was achieved every 5-8 min (range 13-20%). An in vivo (13)C succinate image of a rat was produced.
Conclusion: PASADENA spin hyperpolarization of SUC to 15.3% in average was demonstrated (37,400 fold signal enhancement at 4.7 T). The biological fate of (13)C succinate, a normally occurring cellular intermediate, might be monitored with enhanced sensitivity.
Figures
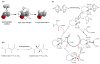
 ) is added to the precursor (
) is added to the precursor ( ) by catalytic hydrogenation; (center) manipulations of the spins of the molecule by spin order transfer r.f. pulse sequence, involving the 2JCHa,3 JCHb,3 JHaHb couplings; (right) net spin polarization is formed on 13C. (b) Hydrogenation of precursor FUM forms the product SUC. (c) Hydrogenation reaction cycle of Rhodium based catalyst: the norbornadiene moeity is hydrogenated and becomes labile and combines with the bisphosphine ligand to form the catalyst. The PASADENA precursor attaches itself to this active catalyst and hydrogenation occurs by addition [15,16]
) by catalytic hydrogenation; (center) manipulations of the spins of the molecule by spin order transfer r.f. pulse sequence, involving the 2JCHa,3 JCHb,3 JHaHb couplings; (right) net spin polarization is formed on 13C. (b) Hydrogenation of precursor FUM forms the product SUC. (c) Hydrogenation reaction cycle of Rhodium based catalyst: the norbornadiene moeity is hydrogenated and becomes labile and combines with the bisphosphine ligand to form the catalyst. The PASADENA precursor attaches itself to this active catalyst and hydrogenation occurs by addition [15,16]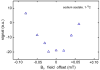

References
-
- Bowers CR, Weitekamp DP. Transformation of symmetrization order to nuclear-spin magnetization by chemical-reaction and nuclear-magnetic-resonance. Phys Rev Lett. 1986;57:2645–2648. - PubMed
-
- Bowers CR, Weitekamp DP. Para-hydrogen and synthesis allow dramatically enhanced nuclear alignment. J Am Chem Soc. 1987;109:5541–5542.
-
- Golman K, Axelsson O, Johannesson H, Mansson S, Olofsson C, Petersson JS. Parahydrogen-induced polarization in imaging: subsecond C-13 angiography. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Born M, Heisenberg W. The quantum theory of molecules. Annalen Der Physik. 1924;74:1–31.
-
- Bonhoeffer KF, Harteck P. Experiments on para-hydrogen and ortho-hydrogen. Naturwissenschaften. 1929;17:182–182.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

