Large-scale analysis of thermostable, mammalian proteins provides insights into the intrinsically disordered proteome
- PMID: 19067583
- PMCID: PMC2760310
- DOI: 10.1021/pr800308v
Large-scale analysis of thermostable, mammalian proteins provides insights into the intrinsically disordered proteome
Abstract
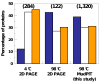
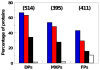
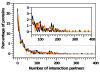
Intrinsically disordered proteins are predicted to be highly abundant and play broad biological roles in eukaryotic cells. In particular, by virtue of their structural malleability and propensity to interact with multiple binding partners, disordered proteins are thought to be specialized for roles in signaling and regulation. However, these concepts are based on in silico analyses of translated whole genome sequences, not on large-scale analyses of proteins expressed in living cells. Therefore, whether these concepts broadly apply to expressed proteins is currently unknown. Previous studies have shown that heat-treatment of cell extracts lead to partial enrichment of soluble, disordered proteins. On the basis of this observation, we sought to address the current dearth of knowledge about expressed, disordered proteins by performing a large-scale proteomics study of thermostable proteins isolated from mouse fibroblast cells. With the use of novel multidimensional chromatography methods and mass spectrometry, we identified a total of 1320 thermostable proteins from these cells. Further, we used a variety of bioinformatics methods to analyze the structural and biological properties of these proteins. Interestingly, more than 900 of these expressed proteins were predicted to be substantially disordered. These were divided into two categories, with 514 predicted to be predominantly disordered and 395 predicted to exhibit both disordered and ordered/folded features. In addition, 411 of the thermostable proteins were predicted to be folded. Despite the use of heat treatment (60 min at 98 degrees C) to partially enrich for disordered proteins, which might have been expected to select for small proteins, the sequences of these proteins exhibited a wide range of lengths (622 +/- 555 residues (average length +/- standard deviation) for disordered proteins and 569 +/- 598 residues for folded proteins). Computational structural analyses revealed several unexpected features of the thermostable proteins: (1) disordered domains and coiled-coil domains occurred together in a large number of disordered proteins, suggesting functional interplay between these domains; and (2) more than 170 proteins contained lengthy domains (>300 residues) known to be folded. Reference to Gene Ontology Consortium functional annotations revealed that, while disordered proteins play diverse biological roles in mouse fibroblasts, they do exhibit heightened involvement in several functional categories, including, cytoskeletal structure and cell movement, metabolic and biosynthetic processes, organelle structure, cell division, gene transcription, and ribonucleoprotein complexes. We believe that these results reflect the general properties of the mouse intrinsically disordered proteome (IDP-ome) although they also reflect the specialized physiology of fibroblast cells. Large-scale identification of expressed, thermostable proteins from other cell types in the future, grown under varied physiological conditions, will dramatically expand our understanding of the structural and biological properties of disordered eukaryotic proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Dunker AK, Obradovic Z, Romero P, Garner EC, Brown CJ. Intrinsic protein disorder in complete genomes. Genome Inform Ser Workshop Genome Inform. 2000;11:161–71. - PubMed
-
- Oldfield CJ, Cheng Y, Cortese MS, Brown CJ, Uversky VN, Dunker AK. Comparing and combining predictors of mostly disordered proteins. Biochemistry. 2005;44:1989–2000. - PubMed
-
- Dunker AK, Brown CJ, Lawson JD, Iakoucheva LM, Obradovic Z. Intrinsic disorder and protein function. Biochemistry. 2002;41:6573–82. - PubMed
-
- Dyson HJ, Wright PE. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:197–208. - PubMed
-
- Minezaki Y, Homma K, Kinjo AR, Nishikawa K. Human transcription factors contain a high fraction of intrinsically disordered regions essential for transcriptional regulation. J Mol Biol. 2006;359:1137–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

