Montelukast inhibits neutrophil pro-inflammatory activity by a cyclic AMP-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 19068077
- PMCID: PMC2697768
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00012.x
Montelukast inhibits neutrophil pro-inflammatory activity by a cyclic AMP-dependent mechanism
Abstract
Background and purpose: The objective of this study was to characterize the effects of the cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, montelukast (0.1-2 micromol x L(-1)), on Ca(2+)-dependent pro-inflammatory activities, cytosolic Ca(2+) fluxes and intracellular cAMP in isolated human neutrophils activated with the chemoattractants, N-formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine (1 micromol x L(-1)) and platelet-activating factor (200 nmol x L(-1)).
Experimental approach: Generation of reactive oxygen species was measured by lucigenin- and luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence, elastase release by a colourimetric assay, leukotriene B(4) and cAMP by competitive binding ELISA procedures, and Ca(2+) fluxes by fura-2/AM-based spectrofluorimetric and radiometric ((45)Ca(2+)) procedures.
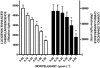
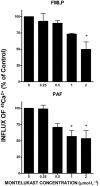
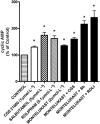
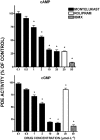
Key results: Pre-incubation of neutrophils with montelukast resulted in dose-related inhibition of the generation of reactive oxygen species and leukotriene B(4) by chemoattractant-activated neutrophils, as well as release of elastase, all of which were maximal at 2 micromol x L(-1) (mean percentages of the control values of 30 +/- 1, 12 +/- 3 and 21 +/- 3 respectively; P < 0.05). From a mechanistic perspective, treatment of chemoattractant-activated neutrophils with montelukast resulted in significant reductions in both post-peak cytosolic Ca(2+) concentrations and store-operated Ca(2+) influx. These montelukast-mediated alterations in Ca(2+) handling by the cells were associated with a significant elevation in basal cAMP levels, which resulted from inhibition of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases.
Conclusions and implications: Montelukast, primarily a cysteinyl leukotriene (CysLT(1)) receptor antagonist, exhibited previously undocumented, secondary, neutrophil-directed anti-inflammatory properties, which appeared to be cAMP-dependent.
Figures



References
-
- Ali H, Sozzani S, Fisher I, Barr AJ, Richardson RM, Haribabu B, et al. Differential regulation of formyl peptide and platelet-activating factor receptors: role of phospholipase Cβ3 phosphorylation by protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:11012–11016. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Drug Review. Asthma. Montelukast, drugs in context. Part E. Respir Med Infect. 2004;1:1–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

