Role of ionotropic cannabinoid receptors in peripheral antinociception and antihyperalgesia
- PMID: 19070372
- PMCID: PMC2863326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2008.10.008
Role of ionotropic cannabinoid receptors in peripheral antinociception and antihyperalgesia
Abstract
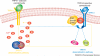
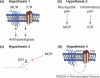
Despite the wealth of information on cannabinoid-induced peripheral antihyperalgesic and antinociceptive effects in many pain models, the molecular mechanism(s) for these actions remains unknown. Although metabotropic cannabinoid receptors have important roles in many pharmacological actions of cannabinoids, recent studies have led to the recognition of a family of at least five ionotropic cannabinoid receptors (ICRs). The known ICRs are members of the family of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels and include TRPV1, TRPV2, TRPV4, TRPM8 and TRPA1. Cannabinoid activation of ICRs can result in desensitization of the TRPA1 and TRPV1 channel activities, inhibition of nociceptors and antihyperalgesia and antinociception in certain pain models. Thus, cannabinoids activate both metabotropic and ionotropic mechanisms to produce peripheral analgesic effects. Here, we provide an overview of the pharmacology of TRP channels as ICRs.
Figures
References
-
- Matsuda LA, et al. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990;346:561–564. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda LA. Molecular aspects of cannabinoid receptors. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 1997;11:143–166. - PubMed
-
- Kim SR, et al. Roles of transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 and cannabinoid type 1 receptors in the brain: neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007;35:245–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

