Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition with MK0431 improves islet graft survival in diabetic NOD mice partially via T-cell modulation
- PMID: 19073764
- PMCID: PMC2646063
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-1101
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition with MK0431 improves islet graft survival in diabetic NOD mice partially via T-cell modulation
Abstract
Objective: The endopeptidase dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) has been shown to NH2-terminally truncate incretin hormones, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, and glucagon-like peptide-1, thus ablating their ability to potentiate glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Increasing the circulating levels of incretins through administration of DPP-IV inhibitors has therefore been introduced as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. DPP-IV inhibitor treatment has also been shown to preserve islet mass in rodent models of type 1 diabetes. The current study was initiated to define the effects of the DPP-IV inhibitor sitagliptin (MK0431) on transplanted islet survival in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice, an autoimmune type 1 diabetes model.
Research design and methods: Effects of MK0431 on islet graft survival in diabetic NOD mice were determined with metabolic studies and micropositron emission tomography imaging, and its underlying molecular mechanisms were assessed.
Results: Treatment of NOD mice with MK0431 before and after islet transplantation resulted in prolongation of islet graft survival, whereas treatment after transplantation alone resulted in small beneficial effects compared with nontreated controls. Subsequent studies demonstrated that MK0431 pretreatment resulted in decreased insulitis in diabetic NOD mice and reduced in vitro migration of isolated splenic CD4+ T-cells. Furthermore, in vitro treatment of splenic CD4+ T-cells with DPP-IV resulted in increased migration and activation of protein kinase A (PKA) and Rac1.
Conclusions: Treatment with MK0431 therefore reduced the effect of autoimmunity on graft survival partially by decreasing the homing of CD4+ T-cells into pancreatic beta-cells through a pathway involving cAMP/PKA/Rac1 activation.
Figures
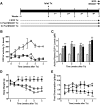
 and *: Post MK0431 Tx. ▪ and •: Pre MK0431 Tx.
and *: Post MK0431 Tx. ▪ and •: Pre MK0431 Tx.
 and *: Post MK0431 Tx. ▪ and •: Pre MK0431 Tx.
and *: Post MK0431 Tx. ▪ and •: Pre MK0431 Tx.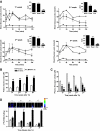
 , Post MK0431 Tx; ▪, Pre MK0431 Tx. (Please see
, Post MK0431 Tx; ▪, Pre MK0431 Tx. (Please see 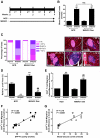


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV with sitagliptin (MK0431) prolongs islet graft survival in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.Diabetes. 2008 May;57(5):1331-9. doi: 10.2337/db07-1639. Epub 2008 Feb 25. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18299314
-
Sitagliptin (MK0431) inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV decreases nonobese diabetic mouse CD4+ T-cell migration through incretin-dependent and -independent pathways.Diabetes. 2010 Jul;59(7):1739-50. doi: 10.2337/db09-1618. Epub 2010 Apr 5. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20368408 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of DPP-IV inhibition in NOD mice with overt diabetes.Folia Biol (Praha). 2013;59(3):116-22. Folia Biol (Praha). 2013. PMID: 23890479
-
Inhibition of DPP-4: a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Apr;23(4):919-31. doi: 10.1185/030079906x162746. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17407649 Review.
-
Sitagliptin: Profile of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Drugs Today (Barc). 2007 Jan;43(1):13-25. doi: 10.1358/dot.2007.43.1.1043909. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007. PMID: 17315049 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of gastric inhibitory polypeptide and its subsequent fate: Personal reflections.J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Apr;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):4-7. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12480. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27186348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor sitagliptin alleviates liver inflammation of diabetic mice by acting as a ROS scavenger and inhibiting the NFκB pathway.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Sep 7;7(1):236. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00625-7. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34493714 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Oral Administration of GABA and DPP-4 Inhibitor Prevents Beta Cell Damage and Promotes Beta Cell Regeneration in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jun 20;8:362. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00362. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28676760 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of early versus late enteral nutrition on cell mediated immunity and its relationship with glucagon like peptide-1 in intensive care unit patients: a prospective study.Crit Care. 2013 Jun 20;17(3):R123. doi: 10.1186/cc12795. Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 23786864 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Improving the Function and Engraftment of Transplanted Pancreatic Islets Using Pulsed Focused Ultrasound Therapy.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 16;9(1):13416. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49933-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31527773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brubaker PL, Drucker DJ: Minireview: glucagon-like peptides regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis in the pancreas, gut, and central nervous system. Endocrinology 145: 2653–2659, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Yusta B, Baggio LL, Estall JL, Koehler JA, Holland DP, Li H, Pipeleers D, Ling Z, Drucker DJ: GLP-1 receptor activation improves beta cell function and survival following induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Metab 4: 391–406, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Kim SJ, Choi WS, Han JS, Warnock G, Fedida D, McIntosh CHS: A novel mechanism for the suppression of a voltage-gated potassium channel by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide: protein kinase A-dependent endocytosis. J Biol Chem 280: 28692–28700, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Ehses JA, Casilla VR, Doty T, Pospisilik JA, Winter KD, Demuth HU, Pederson RA, McIntosh CHS: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide promotes beta-(INS-1) cell survival via cyclic adenosine monophosphate-mediated caspase-3 inhibition and regulation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Endocrinology 144: 4433–4445, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

