Phospholipase C-mediated regulation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 channels: implications in active intestinal Ca2+ transport
- PMID: 19073818
- PMCID: PMC2684912
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.108.052449
Phospholipase C-mediated regulation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 channels: implications in active intestinal Ca2+ transport
Abstract
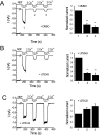
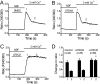
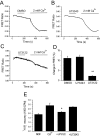
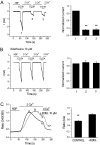
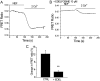
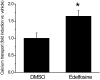
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 (TRPV6) channels play an important role in intestinal Ca(2+) transport. These channels undergo Ca(2+)-induced inactivation. Here we show that Ca(2+) flowing through these channels activates phospholipase C (PLC) leading to the depletion of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)) and formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in TRPV6-expressing cells. PIP(2) depletion was inhibited by the two structurally different PLC inhibitors 1-[6-[[17beta-methoxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-yl]amino]hexyl]-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione (U73122) and edelfosine. Ca(2+)-induced inactivation of TRPV6 was also prevented by the PLC inhibitors in whole-cell patch-clamp experiments. Ca(2+) signals in TRPV6-expressing cells were transient upon restoration of extracellular Ca(2+) but were rendered more sustained by the PLC inhibitors. Finally, intestinal Ca(2+) transport in the everted duodenal sac assay was enhanced by edelfosine. These observations suggest that Ca(2+)-induced inactivation of TRPV6 limits intestinal Ca(2+) absorption and raise the possibility that Ca(2+) absorption can be enhanced pharmacologically by interfering with PLC activation.
Figures
References
-
- Balla T (2001) Pharmacology of phosphoinositides, regulators of multiple cellular functions. Curr Pharm Des 7 475-507. - PubMed
-
- Christakos S, Dhawan P, Benn B, Porta A, Hediger M, Oh GT, Jeung EB, Zhong Y, Ajibade D, Dhawan K, et al. (2007) Vitamin D: molecular mechanism of action. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1116 340-348. - PubMed
-
- Christakos S, Dhawan P, Liu Y, Peng X, and Porta A (2003) New insights into the mechanisms of vitamin D action. J Cell Biochem 88 695-705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

