Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and cognitive impairment
- PMID: 19073839
- PMCID: PMC2730978
- DOI: 10.1177/0891988708327888
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and cognitive impairment
Abstract
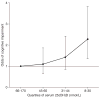
Vitamin D may be of interest in the prevention of cognitive impairment, though previous findings are inconclusive. Participants were 1766 adults aged 65 years and older from the Health Survey for England 2000, a nationally representative population-based study. Cognitive impairment was assessed using the Abbreviated Mental Test Score. The cross-sectional relation of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D quartiles to cognitive impairment was modeled using logistic regression. In all, 212 participants (12%) were cognitively impaired. Odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) for cognitive impairment in the first (8-30 nmol/L), second (31-44 nmol/L), and third (45-65 nmol/L) quartiles of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D compared with the fourth (66-170 nmol/L) were 2.3 (1.4-3.8), 1.4 (0.8-2.4), and 1.1 (0.6-1.9), after adjustment for age, sex, education, ethnicity, season of testing, and additional risk factors for cognitive impairment (P for linear trend = .001). Our data suggest low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with increased odds of cognitive impairment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum albumin concentration and cognitive impairment.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2010 Feb;7(1):91-6. doi: 10.2174/156720510790274392. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2010. PMID: 20205675 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and cognitive impairment in the elderly U.S. population.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011 Jan;66(1):59-65. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glq185. Epub 2010 Nov 1. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21041201 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and cognitive functioning.Int Psychogeriatr. 2016 May;28(5):759-68. doi: 10.1017/S1041610215002252. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Int Psychogeriatr. 2016. PMID: 26691864
-
Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and psychological health in older Chinese men in a cohort study.J Affect Disord. 2011 Apr;130(1-2):251-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2010.10.029. Epub 2010 Nov 5. J Affect Disord. 2011. PMID: 21056909
-
Vitamin D insufficiency and cognitive impairment in Asians: a multi-ethnic population-based study and meta-analysis.J Intern Med. 2016 Sep;280(3):300-11. doi: 10.1111/joim.12491. Epub 2016 Apr 1. J Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 27037788
Cited by
-
Individuals with exceptional longevity manifest a delayed association between vitamin D insufficiency and cognitive impairment.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Jan;62(1):153-8. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12601. Epub 2014 Jan 2. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014. PMID: 24383816 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Alzheimer's Disease: Neurocognition to Therapeutics.Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;2015:192747. doi: 10.1155/2015/192747. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 26351614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D and cognition: Demographic disparities in memory recall and word intrusion in a multiethnic cohort.J Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Jul;106(2):716-725. doi: 10.1177/13872877251344604. Epub 2025 Jul 1. J Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 40518806 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D: do we get enough? A discussion between vitamin D experts in order to make a step towards the harmonisation of dietary reference intakes for vitamin D across Europe.Osteoporos Int. 2013 May;24(5):1567-77. doi: 10.1007/s00198-012-2231-3. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Osteoporos Int. 2013. PMID: 23229471
-
The Role of Vitamin D in the Aging Adult.J Aging Gerontol. 2014 Dec;2(2):60-71. doi: 10.12974/2309-6128.2014.02.02.1. J Aging Gerontol. 2014. PMID: 25893188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Wielen RP, Lowik MR, van den Berg H, et al. Serum vitamin D concentrations among elderly people in Europe. Lancet. 1995;346:207–210. - PubMed
-
- Autier P, Gandini S. Vitamin D supplementation and total mortality: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:1730–1737. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Willett WC, Wong JB, Giovannucci E, Dietrich T, Dawson-Hughes B. Fracture prevention with vitamin D supplementation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 2005;293:2257–2264. - PubMed
-
- Palomer X, Gonzalez-Clemente JM, Blanco-Vaca F, Mauricio D. Role of vitamin D in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10:185–197. - PubMed
-
- McCann JC, Ames BN. Is there convincing biological or behavioral evidence linking vitamin D deficiency to brain dysfunction? FASEB J. 2008;22:982–1001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

