Ubiquitin signals autophagic degradation of cytosolic proteins and peroxisomes
- PMID: 19074260
- PMCID: PMC2602605
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810611105
Ubiquitin signals autophagic degradation of cytosolic proteins and peroxisomes
Abstract
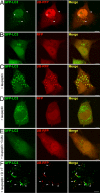
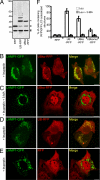
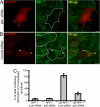
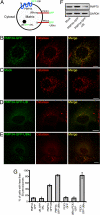
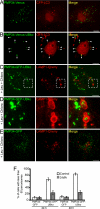
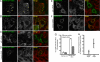
Autophagy is responsible for nonspecific, bulk degradation of cytoplasmic components. Recent work has revealed also that there is specific, autophagic degradation of polyubiquitinated protein aggregates, whose buildup occurs during neurodegenerative disease. Here, we report that simple mono-ubiquitination of normally long-lived cytoplasmic substrates is sufficient to target these substrates for autophagic degradation in mammalian cells. That is, upon their ubiquitination, both small [i.e., red fluorescent protein (RFP)] and large (i.e., peroxisomes) substrates are efficiently targeted to autophagosomes and then degraded within lysosomes upon autophagosome-lysosome fusion. This targeting requires the ubiquitin-binding protein, p62, and is blocked by the Class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, 3-methyladenine (3-MA), or by depletion of the autophagy-related-12 (Atg12) protein homolog. Mammalian cells thus use a common pathway involving ubiquitin and p62 for targeting diverse types of substrates for autophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mizushima N. Autophagy: Process and function. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2861–2873. - PubMed
-
- Liang XH, et al. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. 1999;402:672–676. - PubMed
-
- Hara T, et al. Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature. 2006;441:885–889. - PubMed
-
- Platta HW, Erdmann R. Peroxisomal dynamics. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:474–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

