Activation of leukemia-associated RhoGEF by Galpha13 with significant conformational rearrangements in the interface
- PMID: 19074425
- PMCID: PMC2643521
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M804073200
Activation of leukemia-associated RhoGEF by Galpha13 with significant conformational rearrangements in the interface
Abstract
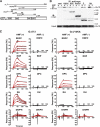
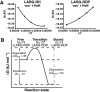
The transient protein-protein interactions induced by guanine nucleotide-dependent conformational changes of G proteins play central roles in G protein-coupled receptor-mediated signaling systems. Leukemia-associated RhoGEF (LARG), a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rho, contains an RGS homology (RH) domain and Dbl homology/pleckstrin homology (DH/PH) domains and acts both as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and an effector for Galpha(13). However, the molecular mechanism of LARG activation upon Galpha(13) binding is not yet well understood. In this study, we analyzed the Galpha(13)-LARG interaction using cellular and biochemical methods, including a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis. The results obtained using various LARG fragments demonstrated that active Galpha(13) interacts with LARG through the RH domain, DH/PH domains, and C-terminal region. However, an alanine substitution at the RH domain contact position in Galpha(13) resulted in a large decrease in affinity. Thermodynamic analysis revealed that binding of Galpha(13) proceeds with a large negative heat capacity change (DeltaCp degrees ), accompanied by a positive entropy change (DeltaS degrees ). These results likely indicate that the binding of Galpha(13) with the RH domain triggers conformational rearrangements between Galpha(13) and LARG burying an exposed hydrophobic surface to create a large complementary interface, which facilitates complex formation through both GAP and effector interfaces, and activates the RhoGEF. We propose that LARG activation is regulated by an induced-fit mechanism through the GAP interface of Galpha(13).
Figures
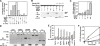
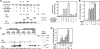
Similar articles
-
A conserved hydrophobic surface of the LARG pleckstrin homology domain is critical for RhoA activation in cells.Cell Signal. 2009 Nov;21(11):1569-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jun 26. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19560536 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of p115-RhoGEF requires direct association of Gα13 and the Dbl homology domain.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):25490-500. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.333716. Epub 2012 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22661716 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor promotes G alpha q-coupled activation of RhoA.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;22(12):4053-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4053-4061.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12024019 Free PMC article.
-
The GAPs, GEFs, and GDIs of heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunits.Int J Biol Sci. 2005;1(2):51-66. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.1.51. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Int J Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15951850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and function of regulator of G protein signaling homology domains.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009;86:75-113. doi: 10.1016/S1877-1173(09)86004-3. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009. PMID: 20374714 Review.
Cited by
-
G protein activation without a GEF in the plant kingdom.PLoS Genet. 2012 Jun;8(6):e1002756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002756. Epub 2012 Jun 28. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22761582 Free PMC article.
-
A Gα12-specific Binding Domain in AKAP-Lbc and p114RhoGEF.J Mol Signal. 2016 Sep 9;11:3. doi: 10.5334/1750-2187-11-3. J Mol Signal. 2016. PMID: 31051012 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved hydrophobic surface of the LARG pleckstrin homology domain is critical for RhoA activation in cells.Cell Signal. 2009 Nov;21(11):1569-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jun 26. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19560536 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction kinetics between p115-RhoGEF and Gα13 are determined by unique molecular interactions affecting agonist sensitivity.Commun Biol. 2022 Nov 24;5(1):1287. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04224-9. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36434027 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrin-stimulated Gα13 Activation of Rgnef Protein (ArhGEF28) in DLD-1 Colon Carcinoma Cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):15197-209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.628164. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25922072 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

