A role for the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) in folate receptor-mediated endocytosis
- PMID: 19074442
- PMCID: PMC2640977
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M807665200
A role for the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) in folate receptor-mediated endocytosis
Abstract
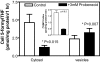
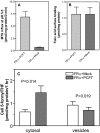
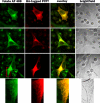
Recently, this laboratory identified a proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT), with optimal activity at low pH. PCFT is critical to intestinal folate absorption and transport into the central nervous system because there are loss-of-function mutations in this gene in the autosomal recessive disorder, hereditary folate malabsorption. The current study addresses the role PCFT might play in another transport pathway, folate receptor (FR)-mediated endocytosis. FRalpha cDNA was transfected into novel PCFT(+) and PCFT(-) HeLa sublines. FRalpha was shown to bind and trap folates in vesicles but with minimal export into the cytosol in PCFT(-) cells. Cotransfection of FRalpha and PCFT resulted in enhanced folate transport into cytosol as compared with transfection of FRalpha alone. Probenecid did not inhibit folate binding to FR, but inhibited PCFT-mediated transport at endosomal pH, and blocked FRalpha-mediated transport into the cytosol. FRalpha and PCFT co-localized to the endosomal compartment. These observations (i) indicate that PCFT plays a role in FRalpha-mediated endocytosis by serving as a route of export of folates from acidified endosomes and (ii) provide a functional role for PCFT in tissues in which it is expressed, such as the choroid plexus, where the extracellular milieu is at neutral pH.
Figures




References
-
- Qiu, A., Jansen, M., Sakaris, A., Min, S. H., Chattopadhyay, S., Tsai, E., Sandoval, C., Zhao, R., Akabas, M. H., and Goldman, I. D. (2006) Cell 127 917–928 - PubMed
-
- Lasry, I., Berman, B., Straussberg, R., Sofer, Y., Bessler, H., Sharkia, M., Glaser, F., Jansen, G., Drori, S., and Assaraf, Y. G. (2008) Blood 112 2055–2061 - PubMed
-
- Geller, J., Kronn, D., Jayabose, S., and Sandoval, C. (2002) Medicine (Baltimore) 81 51–68 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

