Tau deletion exacerbates the phenotype of Niemann-Pick type C mice and implicates autophagy in pathogenesis
- PMID: 19074461
- PMCID: PMC2646181
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddn423
Tau deletion exacerbates the phenotype of Niemann-Pick type C mice and implicates autophagy in pathogenesis
Abstract
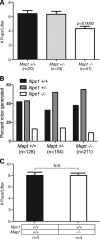
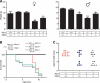
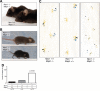
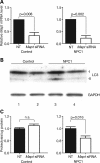
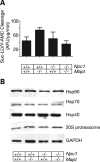
Hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of the microtubule-binding protein tau characterize a diverse array of neurodegenerative disorders. Most of these lack mutations in the encoding MAPT gene, and the role of tau in disease pathogenesis remains controversial. Among these tauopathies is Niemann-Pick type C disease (NPC), a lysosomal storage disorder characterized by progressive neurodegeneration and premature death, most often caused by an inherited deficiency in the intracellular lipid trafficking protein NPC1. To determine the extent to which tau affects NPC pathogenesis, we generated Npc1-/- mice deficient in tau. Unexpectedly, NPC1/tau double null mutants are generated in markedly smaller litters, exhibit an enhanced systemic phenotype and die significantly earlier than NPC1 single null mutants. As autophagy is up-regulated in NPC and protein degradation through this pathway depends on movement along microtubules, we knocked down MAPT expression in NPC1-deficient human fibroblasts and examined effects on this pathway. We show that an acute reduction of tau expression in a cellular model of NPC decreases induction and flux through the autophagic pathway. Our data establish that MAPT deletion exacerbates the NPC phenotype through a mechanism independent of tau protein aggregation and identifies a critical role for tau in the regulation of autophagy in NPC1-deficient cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tau normal function influences Niemann-Pick type C disease pathogenesis in mice and modulates autophagy in NPC1-deficient cells.Autophagy. 2009 May;5(4):548-50. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.4.8364. Autophagy. 2009. PMID: 19332999 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick disease type C1 is a sphingosine storage disease that causes deregulation of lysosomal calcium.Nat Med. 2008 Nov;14(11):1247-55. doi: 10.1038/nm.1876. Epub 2008 Oct 26. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18953351
-
Genetic and pharmacological evidence implicates cathepsins in Niemann-Pick C cerebellar degeneration.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Apr 1;25(7):1434-46. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw025. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 26908626 Free PMC article.
-
The pathogenesis of Niemann-Pick type C disease: a role for autophagy?Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008 Sep 10;10:e26. doi: 10.1017/S146239940800080X. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18782459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Niemann-Pick type C disease: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches.J Neurochem. 2011 Mar;116(5):789-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06976.x. Epub 2011 Jan 7. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 20807315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lessons learnt from animal models: pathophysiology of neuropathic lysosomal storage disorders.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010 Aug;33(4):363-71. doi: 10.1007/s10545-010-9078-6. Epub 2010 May 7. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010. PMID: 20449662
-
Genetic forms of tauopathies: inherited causes and implications of Alzheimer's disease-like TAU pathology in primary and secondary tauopathies.J Neurol. 2024 Jun;271(6):2992-3018. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12314-3. Epub 2024 Mar 30. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38554150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macroautophagy deficiency mediates age-dependent neurodegeneration through a phospho-tau pathway.Mol Neurodegener. 2012 Sep 21;7:48. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-7-48. Mol Neurodegener. 2012. PMID: 22998728 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid-β/Fyn-induced synaptic, network, and cognitive impairments depend on tau levels in multiple mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2011 Jan 12;31(2):700-11. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4152-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21228179 Free PMC article.
-
The many faces of tau.Neuron. 2011 May 12;70(3):410-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.04.009. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 21555069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Higgins J.J., Patterson M.C., Dambrosia J.M., Pikus A.T., Pentchev P.G., Sato S., Brady R.O., Barton N.W. A clinical staging classification for type C Niemann–Pick disease. Neurology. 1992;42:2286–2290. - PubMed
-
- Carstea E.D., Morris J.A., Coleman K.G., Loftus S.K., Zhang D., Cummings C., Gu J., Rosenfeld M.A., Pavan W.J., Krizman D.B., et al. Niemann–Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1997;277:228–231. - PubMed
-
- Ioannou Y.A. Multidrug permeases and subcellular cholesterol transport. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;2:657–668. - PubMed
-
- Davies J.P., Chen F.W., Ioannou Y.A. Transmembrane molecular pump activity of Niemann–Pick C1 protein. Science. 2000;290:2295–2298. - PubMed
-
- Garver W.S., Heidenreich R.A., Erickson R.P., Thomas M.A., Wilson J.M. Localization of the murine Niemann–Pick C1 protein to two distinct intracellular compartments. J. Lipid Res. 2000;41:673–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

