Interleukin-6 overexpression induces pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 19074475
- PMCID: PMC5482545
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.182014
Interleukin-6 overexpression induces pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
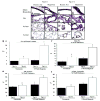
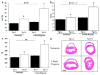
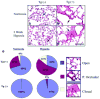
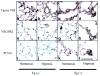
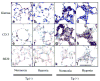
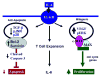
Inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-6 is elevated in the serum and lungs of patients with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH). Several animal models of PAH cite the potential role of inflammatory mediators. We investigated role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of pulmonary vascular disease. Indices of pulmonary vascular remodeling were measured in lung-specific IL-6-overexpressing transgenic mice (Tg(+)) and compared to wild-type (Tg(-)) controls in both normoxic and chronic hypoxic conditions. The Tg(+) mice exhibited elevated right ventricular systolic pressures and right ventricular hypertrophy with corresponding pulmonary vasculopathic changes, all of which were exacerbated by chronic hypoxia. IL-6 overexpression increased muscularization of the proximal arterial tree, and hypoxia enhanced this effect. It also reproduced the muscularization and proliferative arteriopathy seen in the distal arteriolar vessels of PAH patients. The latter was characterized by the formation of occlusive neointimal angioproliferative lesions that worsened with hypoxia and were composed of endothelial cells and T-lymphocytes. IL-6-induced arteriopathic changes were accompanied by activation of proangiogenic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, the proproliferative kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase, proproliferative transcription factors c-MYC and MAX, and the antiapoptotic proteins survivin and Bcl-2 and downregulation of the growth inhibitor transforming growth factor-beta and proapoptotic kinases JNK and p38. These findings suggest that IL-6 promotes the development and progression of pulmonary vascular remodeling and PAH through proproliferative antiapoptotic mechanisms.
Figures
References
-
- Pietra GG, Capron F, Stewart S, Leone O, Humbert M, Robbins IM, Reid LM, Tuder RM. Pathologic assessment of vasculopathies in pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:25S–32S. - PubMed
-
- Morrell NW, Yang X, Upton PD, Jourdan KB, Morgan N, Sheares KK, Trembath RC. Altered Growth Responses of Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells From Patients With Primary Pulmonary Hypertension to Transforming Growth Factor-{beta}1 and Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Circulation. 2001;104:790–795. - PubMed
-
- Blanc-Brude OP, Yu J, Simosa H, Conte MS, Sessa WC, Altieri DC. Inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin regulates vascular injury. Nat Med. 2002;8:987–994. - PubMed
-
- McMurtry MS, Archer SL, Altieri DC, Bonnet S, Haromy A, Harry G, Bonnet S, Puttagunta L, Michelakis ED. Gene therapy targeting survivin selectively induces pulmonary vascular apoptosis and reverses pulmonary arterial hypertension. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2005;115:1479–1491. [see comment] - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

