Estrogen receptor-beta agonist diarylpropionitrile: biological activities of R- and S-enantiomers on behavior and hormonal response to stress
- PMID: 19074580
- PMCID: PMC2659273
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2008-1355
Estrogen receptor-beta agonist diarylpropionitrile: biological activities of R- and S-enantiomers on behavior and hormonal response to stress
Abstract
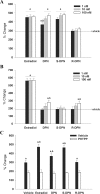
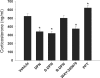
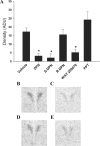
Estrogens have been shown to have positive and negative effects on anxiety and depressive-like behaviors, perhaps explained by the existence of two distinct estrogen receptor (ER) systems, ERalpha and ERbeta. The ERbeta agonist, diarylpropionitrile (DPN) has been shown to have anxiolytic properties in rats. DPN exists as a racemic mixture of two enantiomers, R-DPN and S-DPN. In this study, we compared R-DPN and S-DPN for their in vitro binding affinity, ability to activate transcription in vitro at an estrogen response element, and in vivo endocrine and behavioral responses. In vitro binding studies using recombinant rat ERbeta revealed that S-DPN has a severalfold greater relative binding affinity for ERbeta than does R-DPN. Furthermore, cotransfection of N-38 immortalized hypothalamic cells with an estrogen response element-luc reporter and ERbeta revealed that S-DPN is a potent activator of transcription in vitro, whereas R-DPN is not. Subsequently, we examined anxiety-like behaviors using the open-field test and elevated plus maze or depressive-like behaviors, using the forced swim test. Ovariectomized young adult female Sprague Dawley rats treated with racemic DPN, S-DPN, and the ERbeta agonist, WAY-200070, showed significantly decreased anxiety-like behaviors in both the open-field and elevated plus maze and significantly less depressive-like behaviors in the forced swim test compared with vehicle-, R-DPN-, or propylpyrazoletriol (ERalpha agonist)-treated animals. In concordance with the relative binding affinity and transcriptional potency, these results demonstrate that the S-enantiomer is the biologically active form of DPN. These studies also indicate that estrogen's positive effects on mood, including its anxiolytic and antidepressive actions, are due to its actions at ERbeta.
Figures

References
-
- Green S, Walter P, Kumar V, Krust A, Bornert JM, Argos P, Chambon P 1986 Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature 320:134–139 - PubMed
-
- Zhao C, Toresson G, Xu L, Koehler KF, Gustafsson JA, Dahlman-Wright K 2005 Mouse estrogen receptor β isoforms exhibit differences in ligand selectivity and coactivator recruitment. Biochemistry 44:7936–7944 - PubMed
-
- Shughrue PJ, Lane MV, Merchenthaler I 1997 Comparative distribution of estrogen receptor-α and -β mRNA in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 388:507–525 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

