Interleukin-10 attenuates vascular responses to endothelin-1 via effects on ERK1/2-dependent pathway
- PMID: 19074677
- PMCID: PMC2643883
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00251.2008
Interleukin-10 attenuates vascular responses to endothelin-1 via effects on ERK1/2-dependent pathway
Abstract
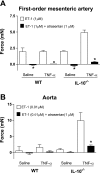
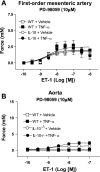
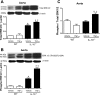
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) is an anti-inflammatory cytokine with protective actions on the vasculature. On the other hand, endothelin (ET)-1 has potent vasoconstrictor, mitogenic, and proinflammatory activities, which have been implicated in the pathophysiology of a number of cardiovascular diseases. We hypothesized that, in a condition where ET-1 expression is upregulated, i.e., on infusion of TNF-alpha, IL-10 confers vascular protection from ET-1-induced injury. Aortic rings and first-order mesenteric arteries from male C57BL/6 (WT) and IL-10-knockout (IL-10(-/-)) mice were treated with human recombinant TNF-alpha (220 ng x kg(-1) x day(-1)) or vehicle (saline) for 14 days. TNF-alpha infusion significantly increased blood pressure in IL-10(-/-), but not WT, mice. TNF-alpha augmented vascular ET-1 mRNA expression in arteries from WT and IL-10(-/-) mice. ET type A (ET(A)) receptor expression was increased in arteries from IL-10(-/-) mice, and TNF-alpha infusion did not change vascular ET(A) receptor expression in control or IL-10(-/-) mice. Aorta and mesenteric arteries from TNF-alpha-infused IL-10(-/-) mice displayed increased contractile responses to ET-1, but not the ET type B receptor agonist IRL-1620. The ET(A) receptor antagonist atrasentan completely abolished responses to ET-1 in aorta and mesenteric vessels, whereas the ERK1/2 inhibitor PD-98059 abrogated increased contractions to ET-1 in arteries from TNF-alpha-infused IL-10(-/-) mice. Infusion of TNF-alpha, as well as knockdown of IL-10 (IL-10(-/-)), induced an increase in total and phosphorylated ERK1/2. These data demonstrate that IL-10 counteracts ET(A)-mediated vascular responses to ET-1, as well as activation of the ERK1/2 pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tail vein injection of mmLDL upregulates mouse mesenteric artery ETB receptors via activation of the ERK1/2 pathway.Vascul Pharmacol. 2017 Sep;96-98:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Vascul Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28797761
-
Endothelin-1 induces pulmonary but not aortic smooth muscle cell migration by activating ERK1/2 MAP kinase.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;88(8):830-9. doi: 10.1139/Y10-059. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20725141
-
Involvement of NO and MEK/ERK pathway in enhancement of endothelin-1-induced mesenteric artery contraction in later-stage type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 May;296(5):H1388-97. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00043.2009. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19286964
-
Vascular endothelin receptor type B: structure, function and dysregulation in vascular disease.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Jul 15;84(2):147-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.03.020. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22484314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel neuroregenerative approach using ET(B) receptor agonist, IRL-1620, to treat CNS disorders.Physiol Res. 2018 Jun 27;67(Suppl 1):S95-S113. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.933859. Physiol Res. 2018. PMID: 29947531 Review.
Cited by
-
Intermittent PTH 1-34 administration improves the marrow microenvironment and endothelium-dependent vasodilation in bone arteries of aged rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Jun 1;124(6):1426-1437. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00847.2017. Epub 2018 Feb 8. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 29420158 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-10 inhibits the in vivo and in vitro adverse effects of TNF-alpha on the endothelium of murine aorta.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Oct;299(4):H1160-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00763.2009. Epub 2010 Jul 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20639218 Free PMC article.
-
TNFα and Reactive Oxygen Signaling in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Hypertension and Atherosclerosis.Am J Hypertens. 2020 Oct 21;33(10):902-913. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpaa089. Am J Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32498083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of uridine adenosine tetraphosphate in the vascular system.Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011;2011:435132. doi: 10.1155/2011/435132. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22110488 Free PMC article.
-
O-GlcNAcylation and Phosphorylation Crosstalk in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Cellular and Therapeutic Significance in Cardiac and Vascular Pathologies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 2;26(7):3303. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073303. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244145 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asadullah K, Sterry W, Volk HD. Interleukin-10 therapy—review of a new approach. Pharmacol Rev 55: 241–269, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Boldrini L, Gisfredi S, Ursino S, Lucchi M, Melfi F, Mussi A, Basolo F, Fontanini G. Tumour necrosis factor-α: prognostic role and relationship with interleukin-8 and endothelin-1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med 17: 887–892, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Kapturczak MH, Wasserfall C, Glushakova OY, Campbell-Thompson M, Deshane JS, Joseph R, Cruz PE, Hauswirth WW, Madsen KM, Croker BP, Berns KI, Atkinson MA, Flotte TR, Tisher CC, Agarwal A. Interleukin 10 attenuates neointimal proliferation and inflammation in aortic allografts by a heme oxygenase-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 7251–7256, 2005. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corder R, Carrier M, Khan N, Klemm P, Vane JR. Cytokine regulation of endothelin-1 release from bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 26 Suppl 3: S56–S58, 1995. - PubMed
-
- D'Angelo G, Adam LP. Inhibition of ERK attenuates force development by lowering myosin light chain phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 282: H602–H610, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

