microRNA expression in the biology, prognosis, and therapy of Waldenström macroglobulinemia
- PMID: 19074725
- PMCID: PMC2943754
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-09-178228
microRNA expression in the biology, prognosis, and therapy of Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Abstract
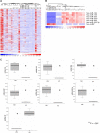
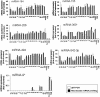
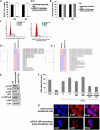
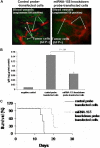
Multilevel genetic characterization of Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is required to improve our understanding of the underlying molecular changes that lead to the initiation and progression of this disease. We performed microRNA-expression profiling of bone marrow-derived CD19(+) WM cells, compared with their normal cellular counterparts and validated data by quantitative reverse-transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). We identified a WM-specific microRNA signature characterized by increased expression of microRNA-363*/-206/-494/-155/-184/-542-3p, and decreased expression of microRNA-9* (ANOVA; P < .01). We found that microRNA-155 regulates proliferation and growth of WM cells in vitro and in vivo, by inhibiting MAPK/ERK, PI3/AKT, and NF-kappaB pathways. Potential microRNA-155 target genes were identified using gene-expression profiling and included genes involved in cell-cycle progression, adhesion, and migration. Importantly, increased expression of the 6 miRNAs significantly correlated with a poorer outcome predicted by the International Prognostic Staging System for WM. We further demonstrated that therapeutic agents commonly used in WM alter the levels of the major miRNAs identified, by inducing downmodulation of 5 increased miRNAs and up-modulation of patient-downexpressed miRNA-9*. These data indicate that microRNAs play a pivotal role in the biology of WM; represent important prognostic marker; and provide the basis for the development of new microRNA-based targeted therapies in WM.
Figures

Comment in
-
MicroRNAs to know in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.Blood. 2009 Apr 30;113(18):4133-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-199828. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19406998 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C-Elegans heterochronic gene Lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to Lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2005;37:766–770. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–531. - PubMed
-
- Roldo C, Missiaglia E, Hagan JP, et al. MicroRNA expression abnormalities in pancreatic endocrine and acinar tumors are associated with distinctive pathologic features and clinical behaviour. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4677–4684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

