Bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: updated time-to-event analyses of the multicenter phase 2 PINNACLE study
- PMID: 19074748
- PMCID: PMC4592328
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdn656
Bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: updated time-to-event analyses of the multicenter phase 2 PINNACLE study
Abstract
Background: We previously reported results of the phase 2, multicenter PINNACLE study, which confirmed the substantial single-agent activity of bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Materials and methods: We report updated time-to-event data, in all patients and by response to treatment, after extended follow-up (median 26.4 months).
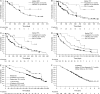
Results: Median time to progression (TTP) was 6.7 months. Median time to next therapy (TTNT) was 7.4 months. Median overall survival (OS) was 23.5 months. In responding patients, median TTP was 12.4 months, median duration of response (DOR) was 9.2 months, median TTNT was 14.3 months, and median OS was 35.4 months. Patients achieving complete response had heterogeneous disease characteristics; among these patients, median TTP and DOR were not reached, and median OS was 36.0 months. One-year survival rate was 69% overall and 91% in responding patients. Median OS from diagnosis was 61.1 months, after median follow-up of 63.7 months. Activity was seen in patients with refractory disease and patients relapsing following high-intensity treatment. Toxicity was generally manageable.
Conclusions: Single-agent bortezomib is associated with lengthy responses and notable survival in patients with relapsed or refractory MCL, with considerable TTP and TTNT in responding patients, suggesting substantial clinical benefit.
Figures
References
-
- Williams ME, Densmore JJ. Biology and therapy of mantle cell lymphoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 2005;17:425–431. - PubMed
-
- Bertoni F, Rinaldi A, Zucca E, et al. Update on the molecular biology of mantle cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 2006;24:22–27. - PubMed
-
- Lenz G, Dreyling M, Hiddemann W. Mantle cell lymphoma: established therapeutic options and future directions. Ann Hematol. 2004;83:71–77. - PubMed
-
- Witzig TE. Current treatment approaches for mantle-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6409–6414. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Lenz G, Hoster E, et al. Early consolidation by myeloablative radiochemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation in first remission significantly prolongs progression-free survival in mantle-cell lymphoma: results of a prospective randomized trial of the European MCL Network. Blood. 2005;105:2677–2684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

