p53-Responsive micrornas 192 and 215 are capable of inducing cell cycle arrest
- PMID: 19074875
- PMCID: PMC2836584
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1569
p53-Responsive micrornas 192 and 215 are capable of inducing cell cycle arrest
Abstract
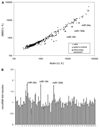
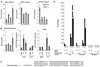
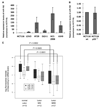
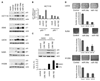
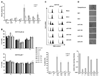
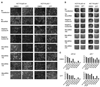
microRNAs provide a novel layer of regulation for gene expression by interfering with the stability and/or translation of specific target mRNAs. Overall levels of microRNAs are frequently down-regulated in cancer cells, and reducing general microRNA processing increases cancerogenesis in transgenic models, suggesting that at least some microRNAs might act as effectors in tumor suppression. Accordingly, the tumor suppressor p53 up-regulates miR-34a, a microRNA that contributes to apoptosis and acute senescence. Here, we used array hybridization to find that p53 induces two additional, mutually related clusters of microRNAs, leading to the up-regulation of miR-192, miR-194, and miR-215. The same microRNAs were detected at high levels in normal colon tissue but were severely reduced in many colon cancer samples. On the other hand, miR-192 and its cousin miR-215 can each contribute to enhanced CDKN1A/p21 levels, colony suppression, cell cycle arrest, and cell detachment from a solid support. These effects were partially dependent on the presence of wild-type p53. Antagonizing endogenous miR-192 attenuated 5-fluorouracil-induced accumulation of p21. Hence, miR-192 and miR-215 can act as effectors as well as regulators of p53; they seem to suppress cancerogenesis through p21 accumulation and cell cycle arrest.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Vousden KH, Lane DP. p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Moll UM, Wolff S, Speidel D, Deppert W. Transcription-independent pro-apoptotic functions of p53. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:631–636. - PubMed
-
- Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science. 2004;303:844–848. - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell. 2008;132:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

