Protective T cell immunity against respiratory syncytial virus is efficiently induced by recombinant BCG
- PMID: 19075247
- PMCID: PMC2634951
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806244105
Protective T cell immunity against respiratory syncytial virus is efficiently induced by recombinant BCG
Abstract
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is one of the leading causes of childhood hospitalization and a major health burden worldwide. Unfortunately, because of an inefficient immunological memory, RSV infection provides limited immune protection against reinfection. Furthermore, RSV can induce an inadequate Th2-type immune response that causes severe respiratory tract inflammation and obstruction. It is thought that effective RSV clearance requires the induction of balanced Th1-type immunity, involving the activation of IFN-gamma-secreting cytotoxic T cells. A recognized inducer of Th1 immunity is Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), which has been used in newborns for decades in several countries as a tuberculosis vaccine. Here, we show that immunization with recombinant BCG strains expressing RSV antigens promotes protective Th1-type immunity against RSV in mice. Activation of RSV-specific T cells producing IFN-gamma and IL-2 was efficiently obtained after immunization with recombinant BCG. This type of T cell immunity was protective against RSV challenge and caused a significant reduction of inflammatory cell infiltration in the airways. Furthermore, mice immunized with recombinant BCG showed no weight loss and reduced lung viral loads. These data strongly support recombinant BCG as an efficient vaccine against RSV because of its capacity to promote protective Th1 immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: A patent application on this work has been filed.
Figures
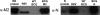
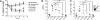
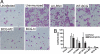
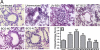


References
-
- Hacking D, Hull J. Respiratory syncytial virus-viral biology and the host response. J Infect. 2002;45:18–24. - PubMed
-
- Mejias A, Chavez-Bueno S, Jafri HS, Ramilo O. Respiratory syncytial virus infections: Old challenges and new opportunities. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24:S189–S196. - PubMed
-
- Chang J, Braciale TJ. Respiratory syncytial virus infection suppresses lung CD8+ T-cell effector activity and peripheral CD8+ T-cell memory in the respiratory tract. Nat Med. 2002;8:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Braciale TJ. Respiratory syncytial virus and T cells: Interplay between the virus and the host adaptive immune system. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2:141–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

