Dysregulation of lipid and amino acid metabolism precedes islet autoimmunity in children who later progress to type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 19075291
- PMCID: PMC2605239
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20081800
Dysregulation of lipid and amino acid metabolism precedes islet autoimmunity in children who later progress to type 1 diabetes
Abstract
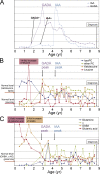
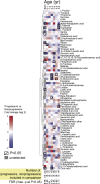
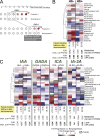
The risk determinants of type 1 diabetes, initiators of autoimmune response, mechanisms regulating progress toward beta cell failure, and factors determining time of presentation of clinical diabetes are poorly understood. We investigated changes in the serum metabolome prospectively in children who later progressed to type 1 diabetes. Serum metabolite profiles were compared between sample series drawn from 56 children who progressed to type 1 diabetes and 73 controls who remained nondiabetic and permanently autoantibody negative. Individuals who developed diabetes had reduced serum levels of succinic acid and phosphatidylcholine (PC) at birth, reduced levels of triglycerides and antioxidant ether phospholipids throughout the follow up, and increased levels of proinflammatory lysoPCs several months before seroconversion to autoantibody positivity. The lipid changes were not attributable to HLA-associated genetic risk. The appearance of insulin and glutamic acid decarboxylase autoantibodies was preceded by diminished ketoleucine and elevated glutamic acid. The metabolic profile was partially normalized after the seroconversion. Autoimmunity may thus be a relatively late response to the early metabolic disturbances. Recognition of these preautoimmune alterations may aid in studies of disease pathogenesis and may open a time window for novel type 1 diabetes prevention strategies.
Figures

Comment in
-
Causes of early-onset type 1 diabetes: toward data-driven environmental approaches.J Exp Med. 2008 Dec 22;205(13):2953-7. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082622. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 19075294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gale, E.A.M. 2002. The rise of childhood type 1 diabetes in the 20th century. Diabetes. 51:3353–3361. - PubMed
-
- Knip, M., R. Veijola, S.M. Virtanen, H. Hyöty, O. Vaarala, and H.K. Åkerblom. 2005. Environmental triggers and determinants of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 54:S125–S136. - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto, J., M. Karvonen, J. Pitkäniemi, E. Virtala, K. Kohtamäki, L. Toivanen, and E. Tuomilehto-Wolf. 1999. Record-high incidence of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in Finnish children. Diabetologia. 42:655–660. - PubMed
-
- Harjutsalo, V., L. Sjöberg, and J. Tuomilehto. 2008. Time trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children: a cohort study. Lancet. 371:1777–1782. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach, P., E. Bonifacio, K. Koczwara, and A.-G. Ziegler. 2005. Natural history of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 54:S25–S31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

